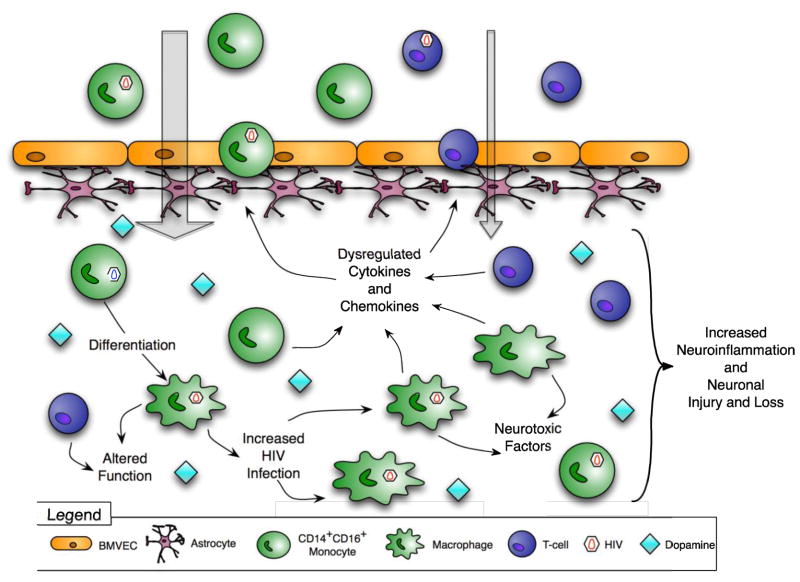
Figure 2. Postulated mechanisms by which dopamine increases CNS inflammation and contributes to HAND.
Drug abuse increases extracellular dopamine in the CNS. Dopamine, alone or with chemokines, increases the transmigration of CD14+CD16+ monocytes across the BBB and may cause T cell influx into the CNS. Elevated dopamine increases HIV replication in macrophages and dysregulates production of cytokines and chemokines. Macrophage and T cell functions are also altered. All of these effects increase neuroinflammation and contribute to HAND.