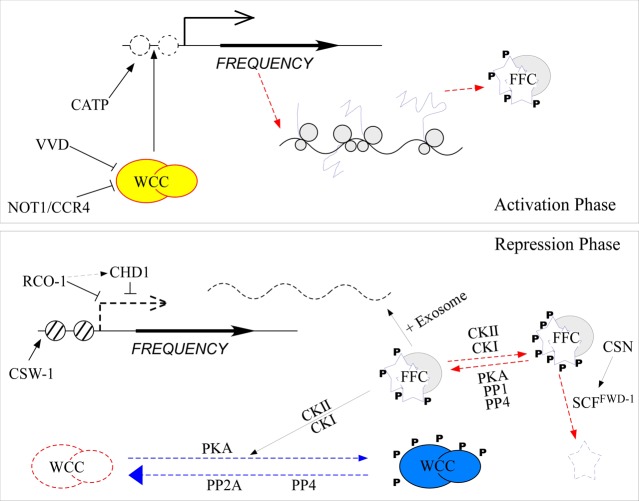
Figure 1.
Model describing the core circadian negative feedback loop of Neurospora. In the activation phase, CATP reduces the histone occupancy on the frq promoter, which promotes WCC binding and activation of frq transcription. After transcription of frq mRNA, the nonoptimal codons in frq mRNA regulate translation speed to allow proper cotranslational folding of FRQ. The resulting FRQ protein is stabilized by its interaction with FRH to form the FFC complex. In the repression phase, FFC recruits casein kinases to phosphorylate PKA-primed WCs and promotes degradation of frq mRNA by the exosome. Phosphorylation of WCC inhibits its DNA binding activity and sequesters it in the cytoplasm. FRQ is progressively phosphorylated by casein kinases and degraded by the ubiquitin/proteasome system, a process that is counterbalanced by the actions of PKA, PP1, and PP4. CSW-1 relocates nucleosomes to suppress frq activation, whereas RCO-1 and CHD1 suppress WC-independent frq transcription to permit WCC-regulated frq transcription. Dephosphorylation of WCC by PP2A and PP4 reactivates WCC to allow reactivation of frq transcription.