Figure 10.
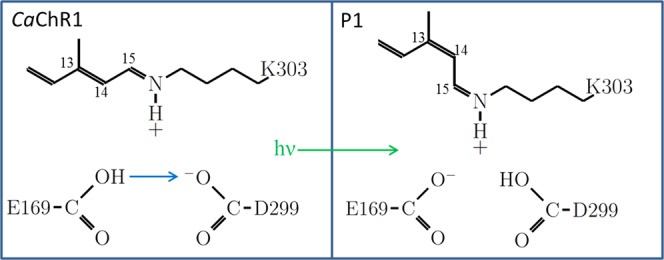
Schematic model showing Glu169 and Asp299 residues that interact with each other through a hydrogen bond formed by the carboxylic acid group of Glu169 and carboxylate group of Asp299. These residues together function as a counterion for the positively charged SB present in the unphotolyzed state of CaChR1. During the initial step in the CaChR1 photocycle (CaChR1 → P1) triggered by light absorption, an all-trans to 13-cis isomerization of the retinylidene chromophore occurs and a proton is transferred from Glu169 to Asp299.
