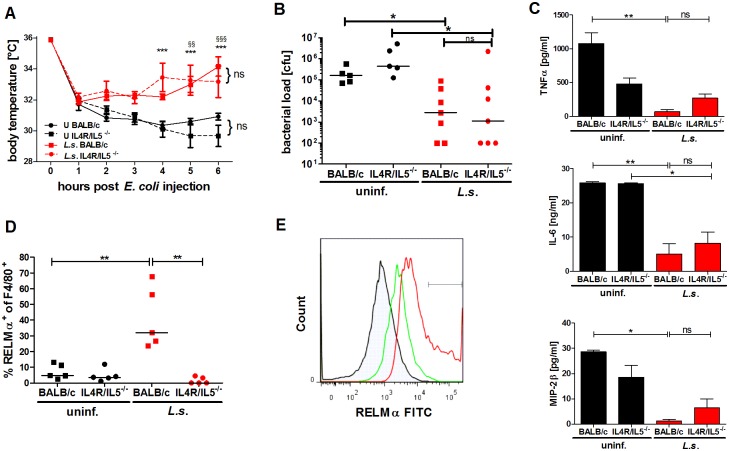
Figure 4. L. sigmodontis-mediated protection against E. coli-induced sepsis is not compromised in AAM-deficient IL-4Rα-/-/IL-5-/- mice.
(A) Kinetic of body temperature in response to i.p. E. coli injection of uninfected (U) and chronic L. sigmodontis (L.s.)-infected wild type and IL-4Rα/IL-5-deficient mice. (B) Peritoneal bacterial load, (C) serum concentrations of TNFα, IL-6 and MIP-2β and (D) frequency of F4/80-positive peritoneal macrophages that are RELMα positive in those animals six hours post E. coli injection. (E) Representative histogram of RELMα fluorescence intensity of F4/80-positive peritoneal macrophages (isotype control (shaded), L.s.-infected IL-4Rα/IL-5-deficient mice (green), L.s.-infected wild type mice (red)). (A-D) Representative dataset from one of two independent experiments with at least 5 mice per group. Data shown in (A) is displayed as mean +/- SEM and was tested for statistical significance by 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc test (asterisks indicate significant differences between L.s.-infected and uninfected IL-4R/IL-5ko mice and paragraphs between L.s.-infected and uninfected wild type mice). (B, C) and (D) data was tested for statistical significance by 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s post-hoc test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.