Figure 2.
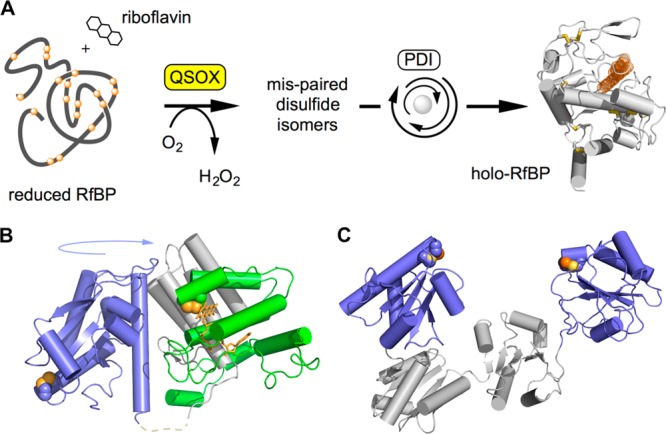
Oxidative protein folding catalyzed by QSOX and reduced PDI. (A) An assay for oxidative folding used in this work. QSOX inserts disulfides into reduced RfBP. Mispaired disulfides are corrected iteratively by PDI, and the fluorescence of free riboflavin is quenched on binding to active apo-RfBP. (B) Structure of an open conformation of QSOX from Trypanosoma brucei. CxxC motifs in the thioredoxin (blue) and ERV (green) domains are shown by solid yellow spheres. These CxxC motifs are brought together during catalysis by a large-scale rotation involving a flexible interdomain linking region (dashed line). Vertebrate QSOXs appear to be mechanistically identical, although they have an additional redox-inactive thioredoxin domain of unknown function. (C) The two CxxC motifs in the a and a′ domains in one (of multiple) conformation of human PDI (PDB 4EL1) are highlighted.
