Figure 3.
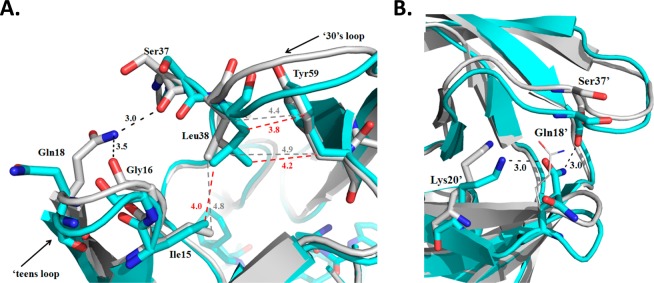
(A) Superposition of PRG48T/L89M-SQV (cyan) with PRWT-SQV (1HXB) (silver). In monomer A of PRG48T/L89M-SQV, hydrogen bonds between Gln18 and Gly16, as well as between Gln18 and Ser37 are lost resulting in approximately 1.5 and 2 Å displacement of the ‘teens and 30’s strand, respectively. The displaced regions are stabilized by new vdw interactions between Leu38, Ile15, and Tyr59. Hydrogen bonds are indicated as dashed lines (black). Vdw interactions are shown as dashed lines for PRG48T/L89M-SQV (red) and PRWT-SQV (gray). (B) Superposition of PRG48T/L89M-SQV (cyan) with PRWT-SQV (silver). Monomer B of PRG48T/L89M-SQV exhibits a greater displacement in the ‘teens region (2.5 Å) and smaller displacement in the 30’s strand (1.25 Å) compared to monomer A. Black dashes indicate hydrogen bonds. In PRG48T/L89M-SQV, there is a new hydrogen bonding interaction between the carbonyl oxygen of Ser37′ and the Nε of Gln18′. The displaced 30’s strand is further stabilized by a new hydrogen bonding interaction between Oε of Gln18′ and the Nζ of Lys20′.
