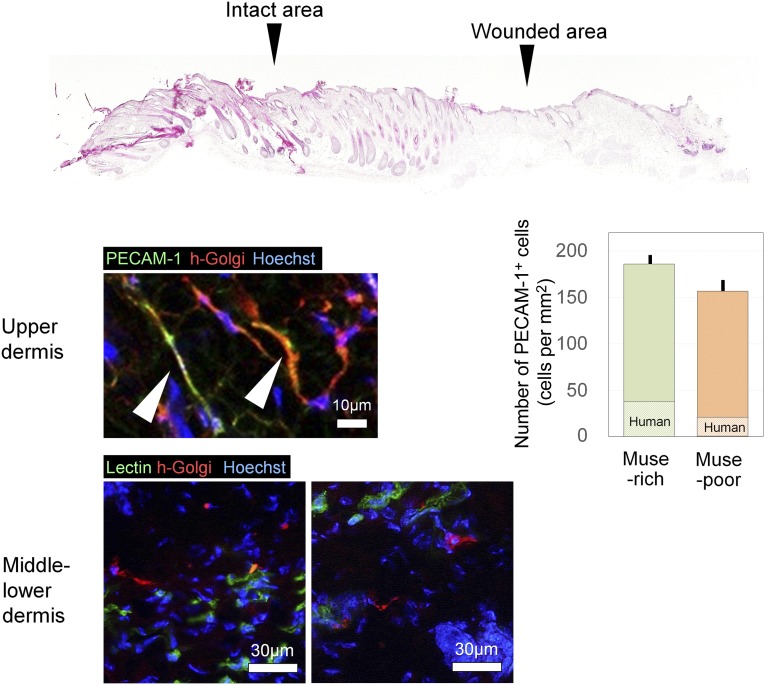
Figure 7.
Immunohistologic findings of differentiation markers expressed by transplanted Muse-rich cells. Double immunohistochemistry was performed for human-specific proteins (human Golgi complex) and differentiation markers (PECAM-1 or isolectin) to characterize transplanted Muse-rich cells at day 14. Some cells expressing human Golgi complex were positive for PECAM-1 or isolectin, suggesting differentiation into vascular endothelial cells in the upper dermis; however, human Golgi complex-positive cells in the middle and lower dermis were negative for PECAM-1 and isolectin. The number of PECAM-1+ cells per microscopic field was counted, with no significant difference between the two groups (p = .144), although the ratio of human-derived cells was higher in the Muse-rich samples (p = .02). Abbreviations: h-Golgi, human Golgi complex; Muse, multilineage-differentiating stress-enduring; PECAM-1, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1.