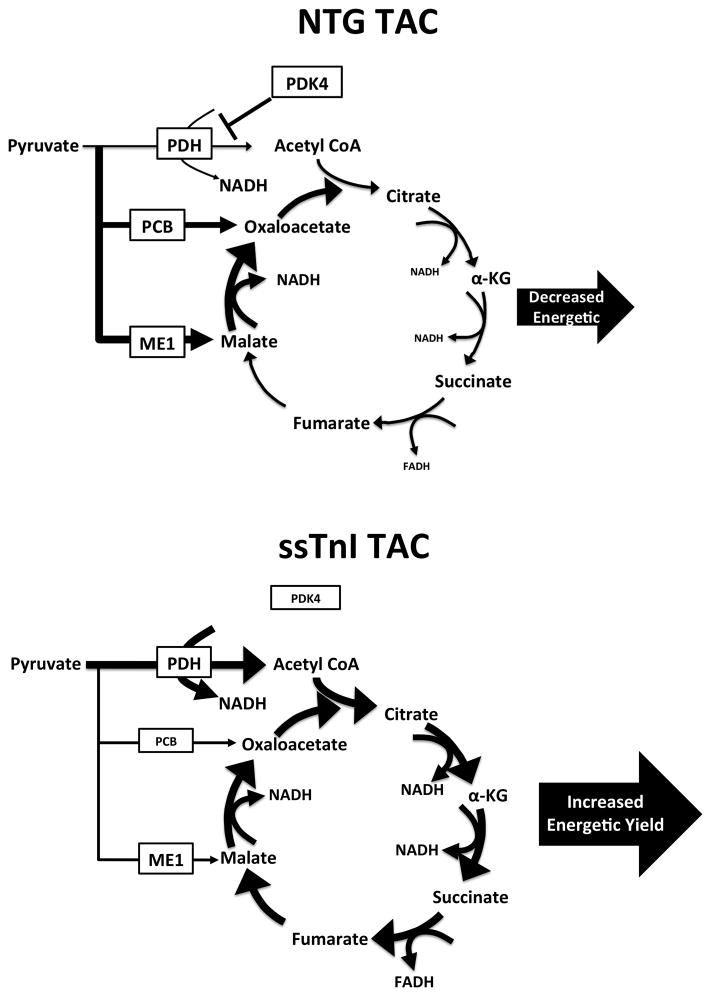
Figure 7. Continued ssTnI expression in the adult heart prevents the upregulation of anaplerotic flux following TAC.
In response to the chronic cardiac stress of pressure overload the heart increases flux of pyruvate through the anaplerotic pathways controlled by malic enzyme (ME1) and pruvate carboxylase (PCB). This decreases the overall energetic yield of pyruvate from the TCA cycle by bypassing key energy generating steps within the mitochondria and results in a significant reduction in energetic efficiency (indicated by reduced flux through NADH generating spans of the TCA cycle). In hearts from ssTnI mice, TAC induces an increase in flux through pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), through a reduction in the expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4). The increase in flux through PDH ensures that pryuvate passes through all spans of the TCA cycle, resulting in greater yield of reducing equivalents (NADH and FADH) for the electron transport chain.