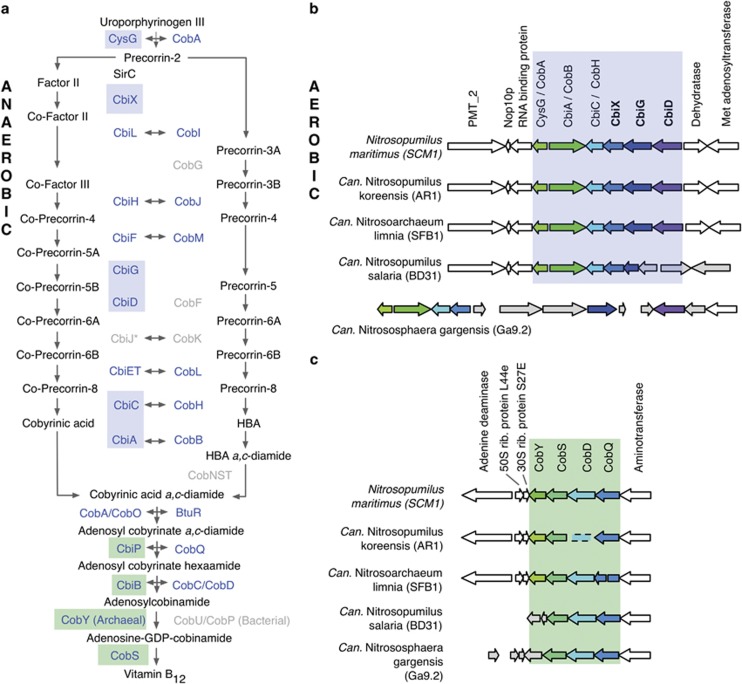
Figure 1.
Identification of the cobalamin synthesis pathway and associated gene clusters in available thaumarchaeotal genomes. The pathway in (a) is adapted from the studies by Moore et al. (2013) and Raux et al. (1999). Horizontal arrows indicate homology between aerobic and anaerobic pathway enzymes. Grey enzyme names were not detected in thaumarchaeotal genomes. *CbiJ is also not present in other known archaeal cobalamin producers and therefore should not be considered an essential gene for this pathway in Thaumarchaeota. (b) A six-member cobalamin synthesis gene cluster with conserved synteny across several thaumarchaeotal genomes. The cluster encodes enzymes (highlighted by blue boxes in (a)) in the upper pathway, and includes three enzymes (bolded) specific to the anaerobic pathway. (c) A four-member gene cluster possessing enzymes (highlighted by green boxes in (a)) corresponding to the final steps of cobalamin synthesis. The apparent missing cobD gene in AR1 may be a genome annotation error given that it appears to be in the genome but may be truncated (data not shown).