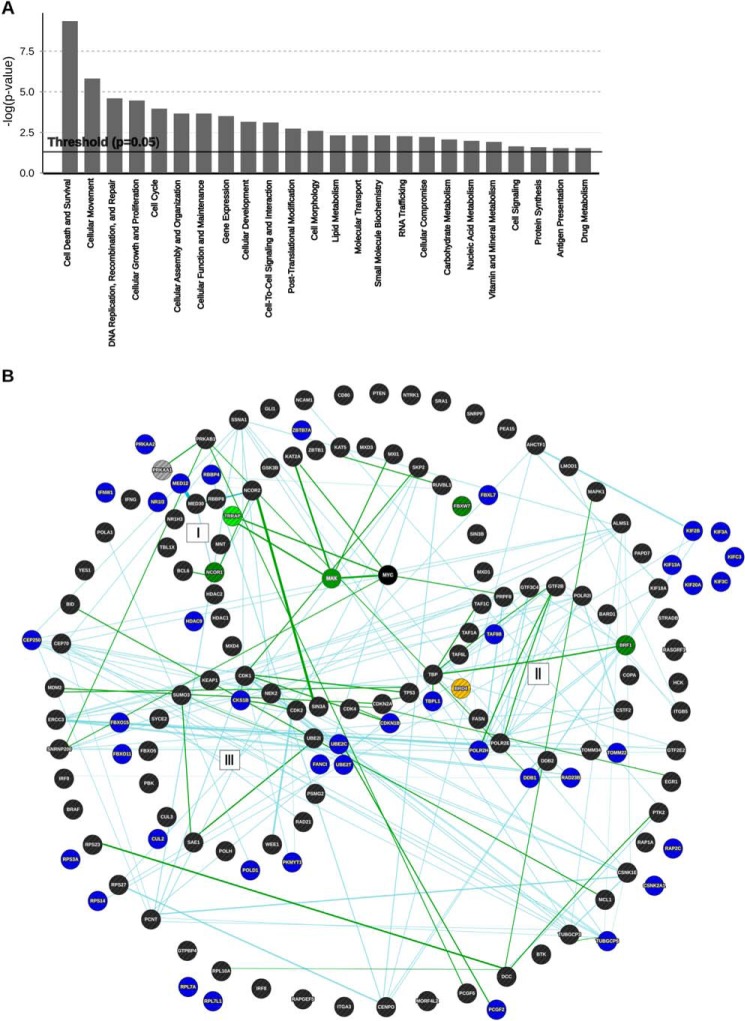
FIGURE 2.
Bioinformatics analysis of synthetic lethal candidates identified with the shRNA screen. A, molecular and cellular functions of the candidate genes. Fisher's exact test was used as a scoring method, and the threshold was set at p = 0.05. B, network analysis showing selected MYCN synthetic lethal genes identified in the shRNA screen (blue) in relation to the network of MYC synthetic lethal genes identified in previous large scale screens (22, 23). The clustering of the genes was adapted from Fig. 3 in Cermelli et al. (29), in which the following functional hubs were identified: (I) MYC-MAX network, (II) components of transcription initiation and elongation complexes, and (III) genes involved in DNA damage repair and cell cycle checkpoints. Genes from the Toyoshima and Kessler screens are depicted in black. MYC synthetic lethal genes that intersect between the “core” genes forming a circle around the MYC-MAX network and the Kessler screen are shown in dark green; those between the core and the Toyoshima screen are light green; those between Kessler and Toyoshima are yellow; and those between our screen and Kessler's are gray. Direct interactions are shown as dark green lines, and indirect interactions are light blue.