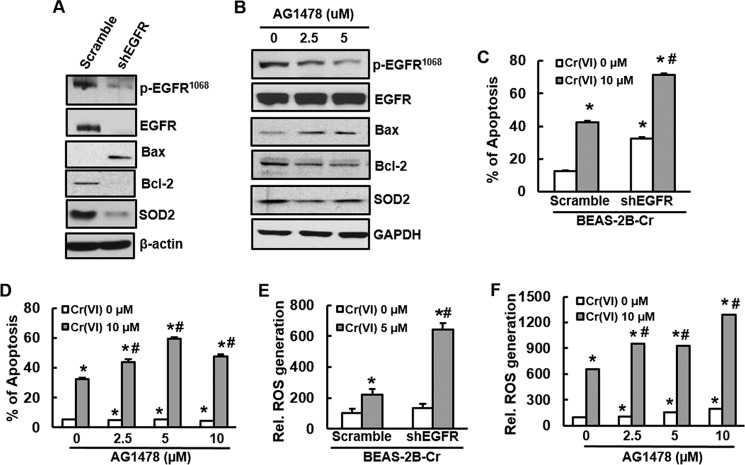
FIGURE 4.
Inhibition of EGFR promotes apoptosis and increases ROS generation in Cr(VI)-transformed cells. A, C, and E, Cr(VI)-transformed cells were stably transfected with shRNA EGFR. A, BEAS-2B-Cr and its stable knockdown of EGFR (shEGFR) were cultured in 10-cm dishes. After 90% confluence, the cells were harvested and subjected to immunoblotting to examine expression of EGFR, apoptotic proteins, or SOD2 using specific antibody. C, Apoptosis analysis. BEAS-2B-Cr with or without EGFR knockdown were treated with 10 μm of Cr(VI) for 24 h. Annexin V-FITC/PI assay was used for apoptosis analysis. E, ROS generation. DCF fluorescence intensity was measured in BEAS-2B-Cr cells with or without knockdown of EGFR in the presence or absence of 5 μm Cr(VI). B, BEAS-2B-Cr cells were treated with different doses of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478 (2.5 and 5.0 μm). After 24 h, the cells were collected for examination of EGFR, Bcl-2, Bax, and SOD2 expression by immunoblotting. D and F, BEAS-2B-Cr cells were pre-treated with different doses of AG1478 (2.5, 5.0, and 10.0 μm) 1 h prior to Cr(VI) treatment (10 μm). After 24 h, the cells were harvested for measurement of apoptosis (D) and ROS generation (F) using flow cytometry and spectrofluorometer, respectively. * and #, p < 0.05 compared with its control cells without Cr(VI) treatment and scramble cells with Cr(VI) treatment.