FIGURE 1.
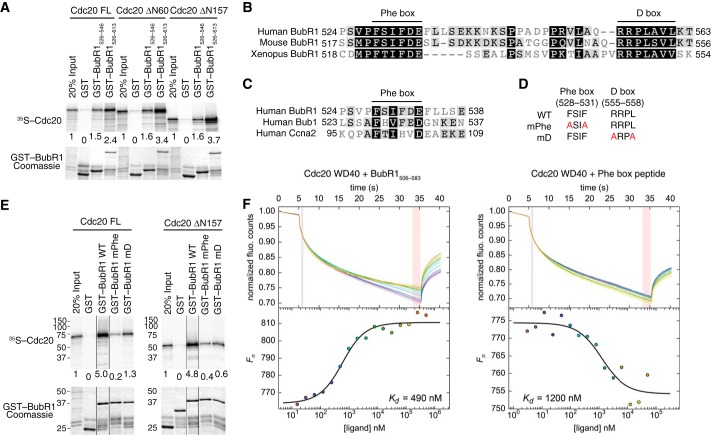
Identification of a conserved Phe box in BubR1 that interacts with Cdc20. A, autoradiograph (top panel) and Coomassie staining (bottom panel) of the input and bound proteins of the binding reactions between GST or GST-BubR1 fragments (bound to beads) and in vitro translated 35S-labeled full-length (FL) or truncated Cdc20. The relative binding intensities are quantified and indicated below each lane. B, sequence alignment of the Phe and D boxes in human, mouse, and Xenopus BubR1 proteins, with high or low similarity residues shaded in black or gray, respectively. C, sequence alignment the Phe boxes of human BubR1, Bub1, and cyclin A2. D, list of Phe and D box mutants (termed mPhe and mD) used in this study. E, autoradiograph (top panel) and Coomassie staining (bottom panel) of the input and bound proteins of the binding reactions between GST or GST-BubR1526–613 WT, mPhe, or mD and 35S-labeled full-length or truncated Cdc20. All samples were run in the same gel. Certain lanes were removed for clarity, and the remaining lanes were spliced together. The relative binding intensities are indicated below each lane. F, microscale thermophoresis analysis of binding of BubR1506–583 (left panel) or a synthetic BubR1 Phe box peptide (right panel) to the Cdc20 WD40 domain. The dissociation constant (Kd) of each binding reaction is indicated. fluo., fluorescence.