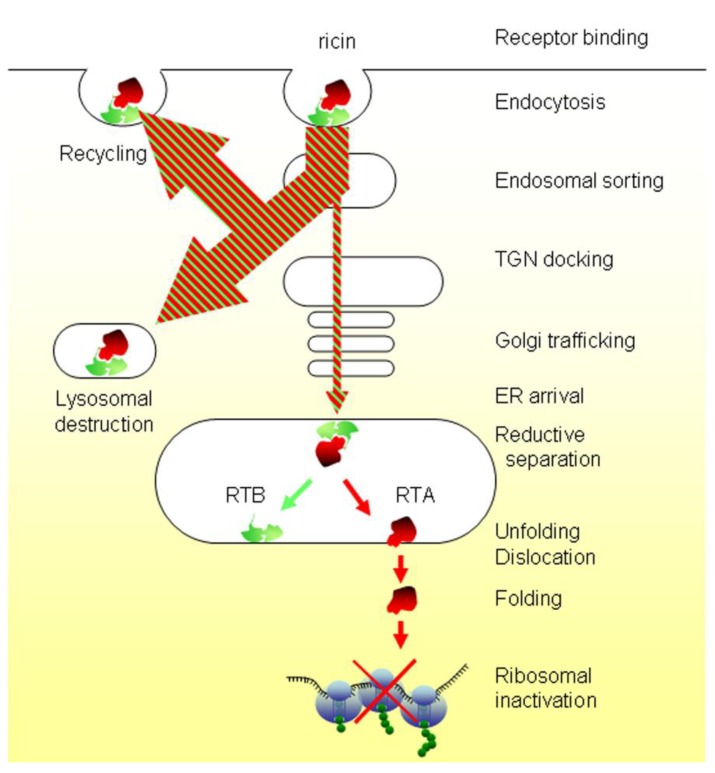
Figure 2.
Intracellular trafficking of ricin. Ricin binds N-glycosylated molecules with available β1→4 linked galactosyls at the plasma membrane and after internalization by endocytosis, traffics via early endosomes, the TGN and the Golgi stack to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where reductive separation of the toxic ricin toxin A (RTA) from the cell-binding ricin toxin B (RTB) occurs. Free RTA retrotranslocates (dislocates), refolds in the cytosol and inhibits protein synthesis by catalytic removal of a key adenine residue on the 28S ribosomal subunit, at the site of EF-2 complex interaction [15]. Following a ribotoxic stress response and activation of multiple signaling pathways [16], ricin-treated cells die apoptotically [17].