Figure 3.
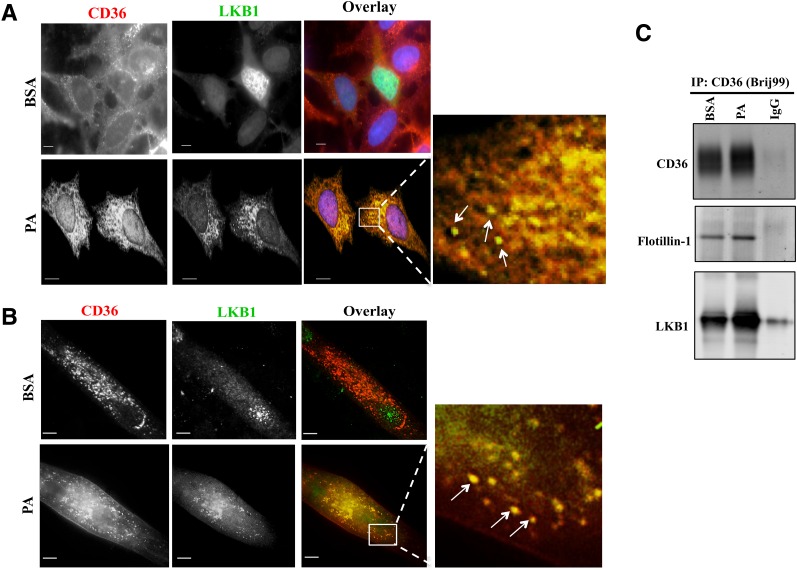
PA induces CD36 association with LKB1. A and B: PA addition relocates LKB1 to cytosolic CD36-positive vesicular structures. Micrographs showing PA-induced redistribution of LKB1 and its colocalization with CD36 in CHO-CD36 cells (A) and in myotubes (B). The cells were serum starved, incubated with 300 μmol/L PA (2:1 BSA) or BSA for 15 min, and stained with anti-CD36 (FA6-152 [Abcam] for CHO; MF3 [AbD Serotec] for myotubes) and anti-LKB1 (5c10; Millipore) antibodies. Images are representative of multiple fields from three experiments. Arrows point to overlap between CD36 and LKB1 within cytoplasmic vesicular structures. Scale bar, 10 μm. C: PA addition results in a CD36-LKB1 association within lipid domains. CHO-CD36 cells, serum starved then incubated with 300 μmol/L PA (2:1 BSA) or BSA for 15 min were lysed with buffer containing 1% Brij99. Equal protein amounts were immunoprecipitated (IP:CD36) using anti-CD36 antibody (AF1955; R&D Systems) and nonimmune IgG as a negative control. Immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and probed for CD36, flotillin-1, and LKB1. Data are representative of two experiments.