Figure 6.
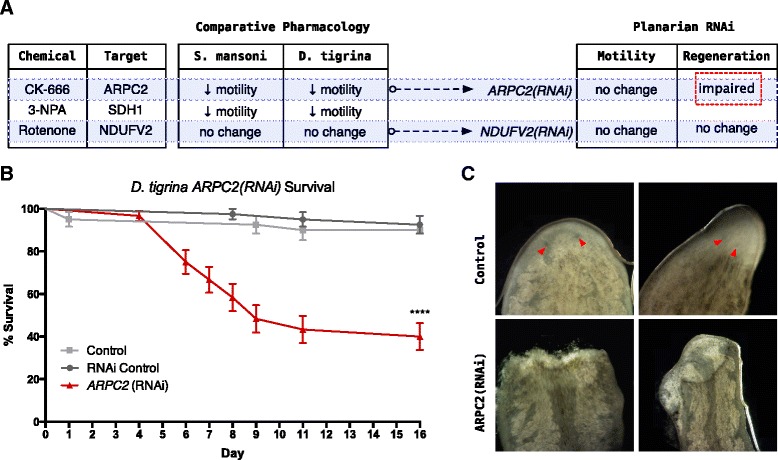
RNAi phenotypes correlate to pharmacology screen. A) Comparative pharmacology led to the selection of ARPC2 (increased motility) and NDUFV2 (no noticeable phenotype) as proof of principle targets for RNAi-mediated knock-down. RNAi of both targets did not bring about any significant changes in planarian motility. However, ARPC2 suppression was lethal to regenerating G. tigrina. These observations correlate to the pharmacology screen where no phenotype was observed with application of NDUFV2 inhibitor, but stark motility phenotypes were observed with ARPC2 chemical inhibitor. B) Survival curves show significantly decreased (P < 0.0001; Log-rank Mantel-Cox test) rates of survival for ARPC2(RNAi) cut worms in comparison to control cut worms. C) Prior to death, caudal fragments of ARPC2(RNAi) cut worms showed impaired sealing of the initial wound and improper blastema formation. Proper eye spot formation can be observed in control worms (red arrows) and is absent in the ARPC2 suppressed worms. These experiments were carried out in duplicate, with at least 10 whole planaria used for motility assays and 20 planarian halves used to monitor regeneration.
