Figure 10.
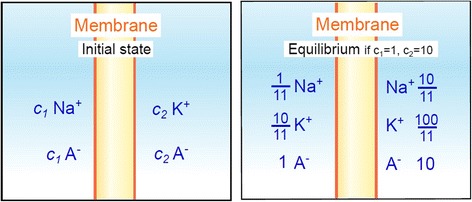
Donnan’s equilibrium. Two solutions containing two different initial concentrations of different salts are separated by a membrane. In this case, the membrane is impermeable to anions but permeable to cations. Donnan thermodynamic calculations and experiments showed that, contrary to what could be initially thought, the two cations do not just interchange with each other until they are equally distributed in the two compartments. Instead, equivalent quantities of both cations cross the membrane; as their initial concentrations are different, the cation which was initially less concentrated proportionally crosses the membrane more than the initially highly concentrated cation.
