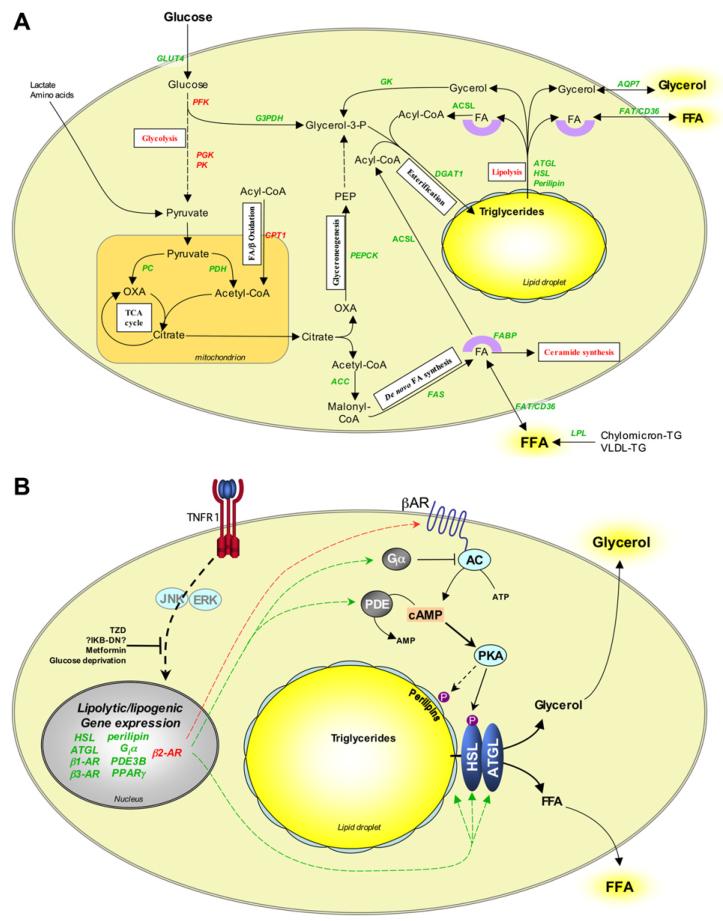
Fig. 3. Effects of TNF-α on adipocyte lipid metabolism and lipolysis.
(A) Pathways involved in adipocyte lipogenesis and their modulation by TNF-α. Adipocytes take up glucose, glycerol and FFA from serum and convert these to triglycerides via numerous biochemical pathways. White boxes indicate the nature of the pathways involved. TNF-α modulates the expression of many of the enzymes and other proteins that regulate these pathways, thereby compromising adipocyte triglyceride storage. (B) Mechanisms of TNF-α-induced lipolysis in adipocytes. During lipolysis triglycerides are hydrolysed into FFA and glycerol. Stimulus-induced lipolysis is mediated by hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), whereas basal lipolysis may be regulated by adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL). Lipolysis is further regulated by the perilipins, a family of phosphoproteins that are localised at the surface of lipid droplets in adipocytes. Perilipins normally inhibit lipolysis by preventing access of lipases to the lipid droplets. PKA stimulates lipolysis by phosphorylating HSL and the perilipins. This activates HSL and enables it to access substrates in the lipid droplets. Downregulation of cAMP by phosphodiesterases (PDE) or stimulation of Giα-coupled receptors abrogates PKA activation and thereby inhibits lipolysis. TNF-α stimulates lipolysis via a glucose-dependent mechanism that likely involves transcriptional effects. These may be mediated via JNK, ERK1/2 and NFκB, resulting in upregulation of cAMP and downregulation of perilipins. Some of these effects, such as downregulation of Giα subtypes, are specific to rodent adipocytes. Arrows and gene names in red and green indicate upregulation and downregulation, respectively. PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FAS, fatty acid synthase; FABP, fatty acid-binding protein; FAT, fatty acid translocase; ACS, aceyl-CoA synthetase long chain; DGAT1, diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1; AQP7, aquaporin 7; GK, glycerol kinase; G3PDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; PFK, phosphofructokinase; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; PK, pyruvate kinase; PC, pyruvate carboxylase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; TCA, tri-carboxylic acid; CPT1 carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; OXA, oxaloacetate; PEP, phosphoenol pyruvate; TG, triglyceride; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein.