Fig. 3.
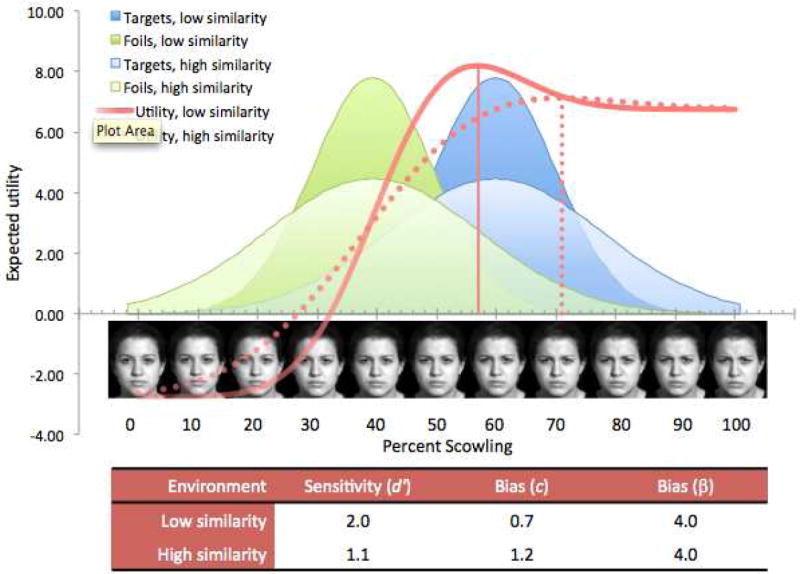
To optimize their performance in a biased environment, perceivers with low sensitivity must adopt a more extreme bias than those with high sensitivity. Comparison of two optimal models that differ in similarity of targets vs. foils illustrates that, to offset the decrement in performance caused by low sensitivity, perceivers with low sensitivity should adopt a more extreme bias (depicted by the rightward shift of the criterion for the “high similarity” utility function; see inset table). Note that bias as measured by beta does not explicitly reflect the difference in behavior. Parameter values provided in Supplemental Material.
