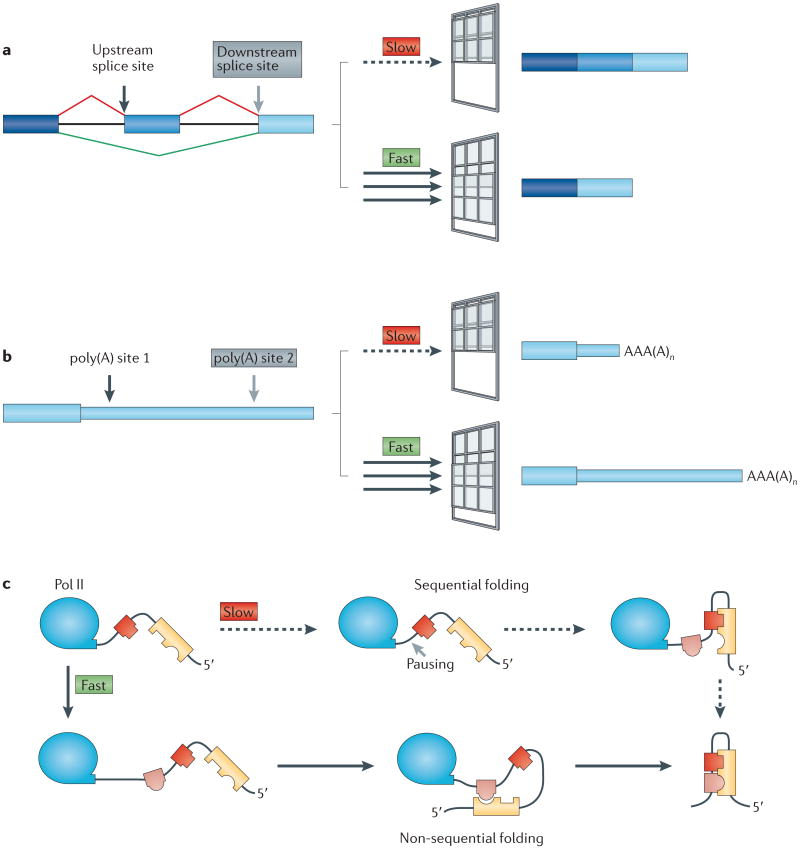
Figure 4. Kinetic coupling of transcription with folding and processing of the pre-mRNA.
Transcription elongation rate determines the length of the ‘window of opportunity’ for an upstream event to occur on the nascent RNA before it must compete with a downstream event. Slow elongation widens the window of opportunity for commitment to processing at upstream splice sites and poly(A) sites. This could lead to inclusion of alternative exons (part a) and 3′end formation at upstream poly(A) sites (part b), which results in mRNAs with shorter 3′untranslated regions. Slow elongation also favours RNA folding by base-pairing of proximal complementary sequences (represented by interlocking shapes) (part c), which results in sequential rather than non-sequential folding72,126. Part c is modified, with permission, from REF. 134 © (2006) Annual Reviews.