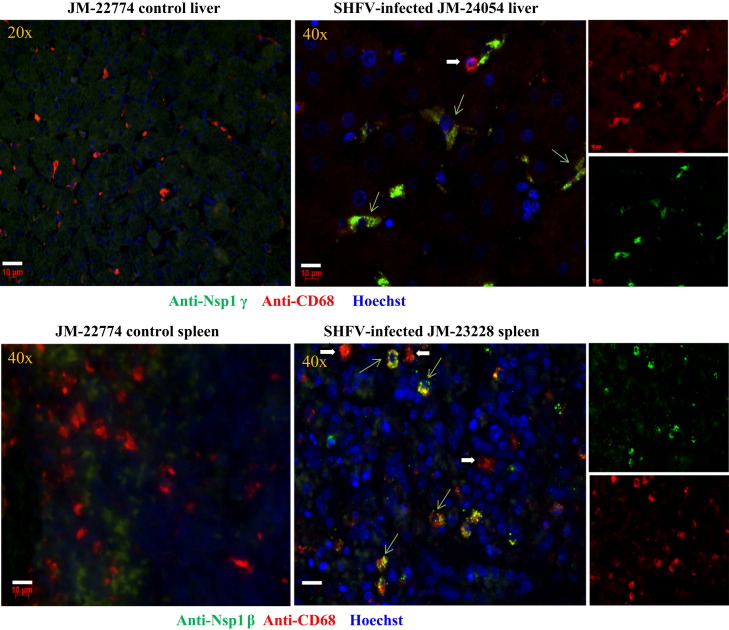
Fig. 4.
Detection of SHFV-infected cells in tissues from SHFV-infected and control Japanese macaques by immunofluorescence. Post-mortem tissue was obtained, formalin-fixed and embedded in paraffin. Sections (5 μm thick) were cut, processed as described in Materials and methods and incubated with a rabbit antibody to SHFV nsp1β or nsp1γ, then biotinylated goat anti-rabbit antibody and then streptavidin Alexa Fluor 488. Next, the sections were incubated with a mouse anti-CD68 antibody, then a biotinylated goat anti-mouse secondary antibody and then streptavidin Alexa Fluor 594. Nuclei were visualized with Hoechst 33258 staining. Cells were visualized using a Zeiss Axioscope 2 plus microscope equipped with a digital camera. Thin green arrows indicate cells detected by both anti-SHFV nonstructural protein and anti-CD68 antibodies. Thick white arrows indicate cells detected only by anti-CD68 antibody. The objective used to capture the image is indicated in the upper left corner, bars=10 μm.