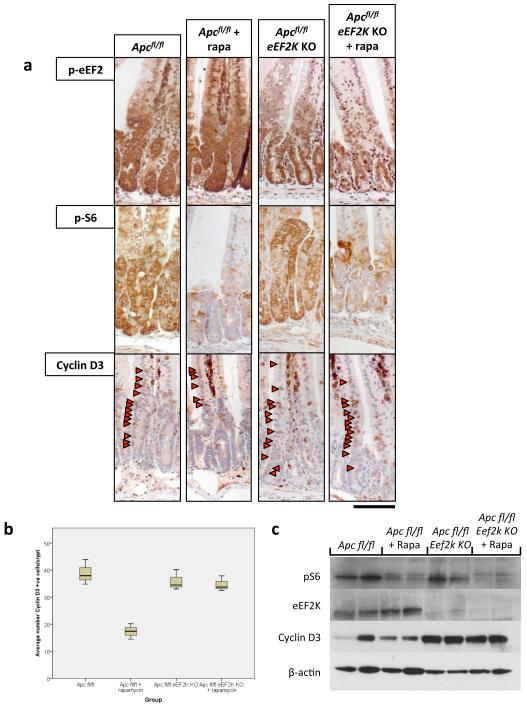
Extended Data Fig. 9. Cyclin D3 is regulated at the level of elongation.
a) Representative IHC of Apcfl/fl intestines with and without Eef2k deletion. Antibodies to eEF2K, phospho-S6, and Cyclin D3 are shown (representative of 3 biological replicates). Following Eef2k KO, Cyclin D3 levels are no longer decreased upon 10mg/kg rapamycin treatment; b) boxplot showing the number of Cyclin D3 positive cells per crypt, 96hrs after Apc deletion, with and without 10mg/kg rapamycin treatment. Graph shows that in Eef2k KO animals, rapamycin no longer reduced Cyclin D3 levels (n=3 biological replicates per group; *p-value≤0.05, Mann Whitney U test); c) western blot analysis of intestinal epithelial cells from Apcfl/fl and Apcfl/fl Eef2k KO, with and without 10mg/kg rapamycin. Antibodies to eEF2K, phospho-S6, Cyclin D3 and β-actin are shown. Each well represents a different mouse from the relevant group. Cyclin D3 levels are no longer reduced following Eef2k deletion. Scale bar = 100μm.