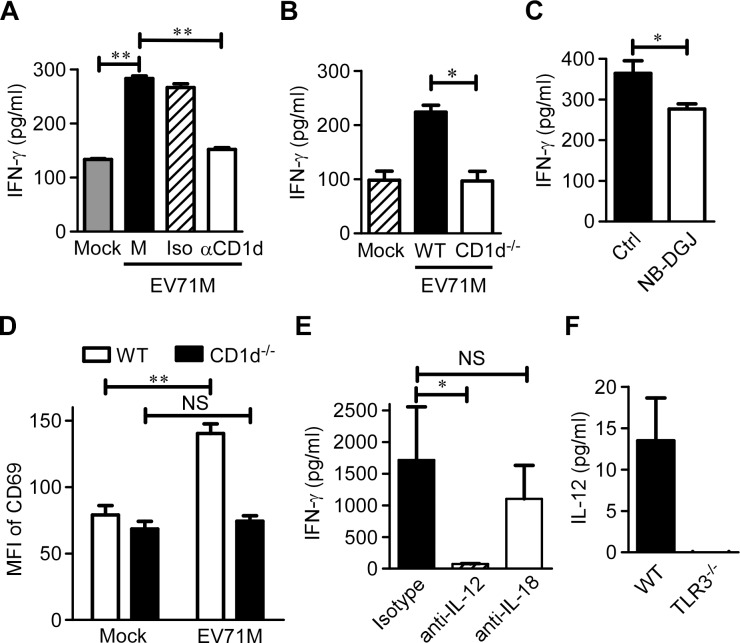
Figure 4. IL-12 and endogenous CD1d antigens are both required for full iNKT cell activation in EV71 infection.
(A) EV71M-infected or-uninfected WT macrophages (Mock) were co-cultured with purified iNKT cells in the presence of neutralizing anti-CD1d (αCD1d), isotype control antibodies (Iso) or medium alone (M). (B) EV71M-infected or –uninfected WT or CD1d-deficient (CD1d-/-) macrophages were co-cultured with purified iNKT cells. (C) EV71-infected WT macrophages were co-cultured with purified iNKT cells in the presence of the lipid synthesis inhibitor NB-DGJ or medium alone. (D) Seven-day-old WT or CD1d-/- neonates (n = 3–5) were adoptively transferred with 5×105 purified iNKT cells or saline control intraperitoneally and infected with 2×105 PFU of EV71M. After 16 hours, splenocytes of saline (mock)-treated or EV71M-infected WT or CD1d-/- mice were stained with TCRβ, CD1d tetramer, CD69 and DAPI. The CD69 MFI levels on iNKT cells are shown. (E) EV71M-infected WT macrophages were co-cultured with purified iNKT cells in the presence of neutralizing anti-IL-12, anti-IL-18 or isotype control antibodies. The IFN-γ concentrations in the 24-hour culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA. (F) The IL-12 (p70) concentrations in the supernatants of WT or TLR3-/- macrophages infected with 10 MOIs of EV71M. All results represent the mean ± SD. NS, not significant; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01. Data are representative of three (A, B, C, E, F) or two (D) independent experiments.