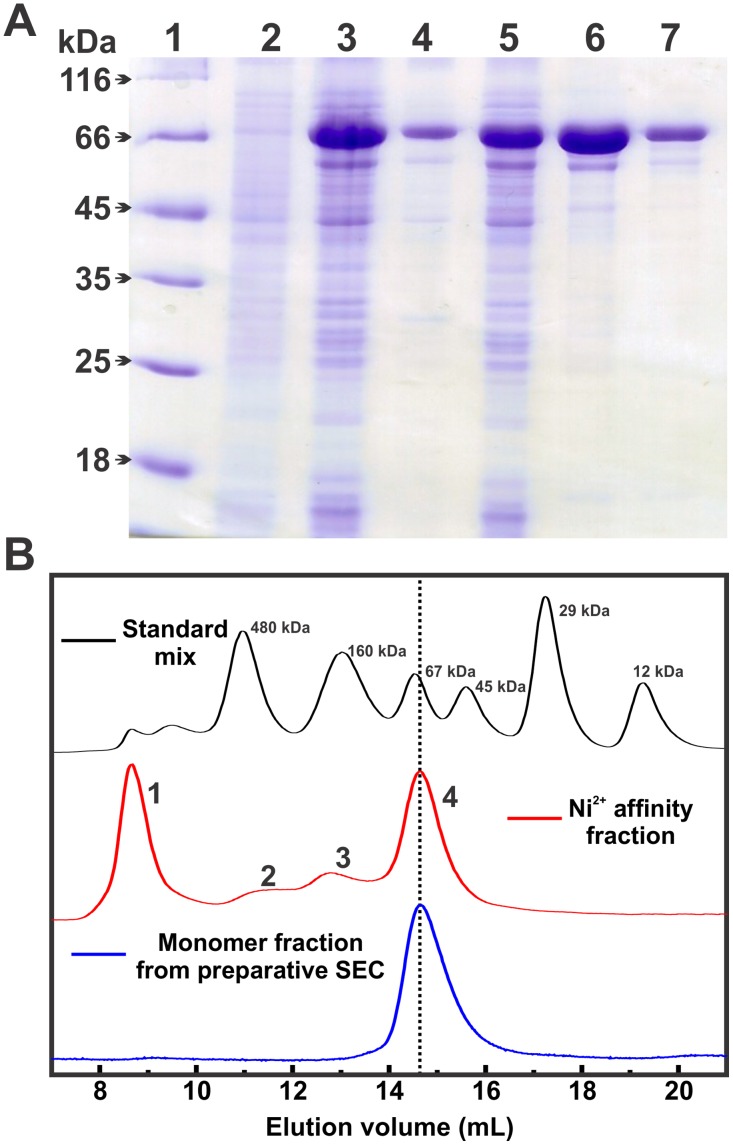
Fig 1. Mortalin production and isolation.
Recombinant human mortalin (pET28a::mtHsp70) was co-expressed with recombinant hHep1 (pET23a::hHep1) in E. coli BL21(DE3) cells. A) SDS-PAGE of the produced and purified recombinant mortalin. 1) MM markers in kDa (left); 2) non-induced bacterial pellet; 3) induced bacterial pellet; 4) pellet of lysed cells; 5) supernatant of lysed cells; 6) fraction obtained from Ni2+ affinity chromatography; and 7) preparative SEC fraction. The final purity of mortalin was higher than 95%. B) aSEC profile of mortalin after Ni2+ affinity chromatography (red line), which showed that mortalin was eluted into four fractions (see text for details). The monomeric fraction (4) was immediately reloaded into the aSEC column and eluted as a monomer (blue line). The standard protein mixture profile is represented by the black line, and the MM of each protein is shown. The vertical dashed line marks the monomeric mortalin elution volume.