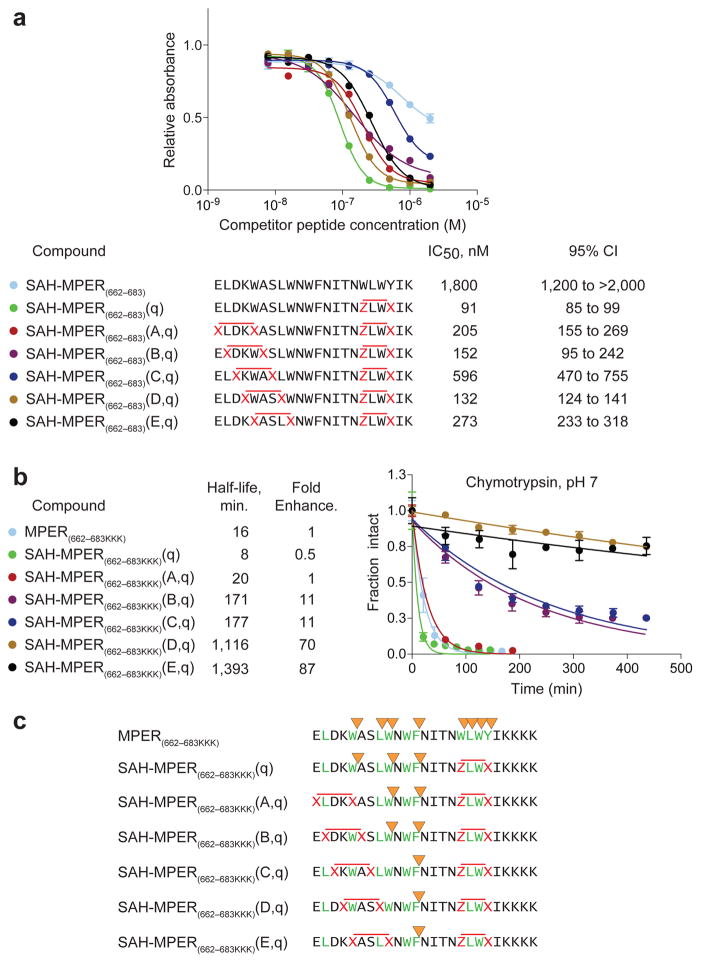
Figure 6. Synthesis, Protease Stability, and 4E10 Binding Activity of Double-stapled SAH-MPER Peptides.
(a) A series of double-stapled SAH-MPER(662-683) peptides were tested for 4E10 binding activity by competitive ELISA assay. (b) Comparative chymotrypsin resistance of SAH-MPER(662-683) peptides, as monitored by LC/MS over time. Proteolysis was performed with SAH-MPER constructs bearing C-terminal KKKs to optimize peptide ionization for MS analysis. Error bars, s.e.m. (n = 3 proteolysis reaction replicates). (c) MS-based peptide fragment analysis identified the sites of chymotrypsin proteolysis. Whereas chymotrypsin sites (yellow arrowheads) located within or adjacent to the installed staples (red X-X, Z-X pairs) were completely protected from proteolysis, the cleavage kinetics for intervening site(s) was progressively slowed (A,q<B,q<C,q<D,q<E,q) by the induced structure of the approaching N-terminal staple (red X-X pairs).