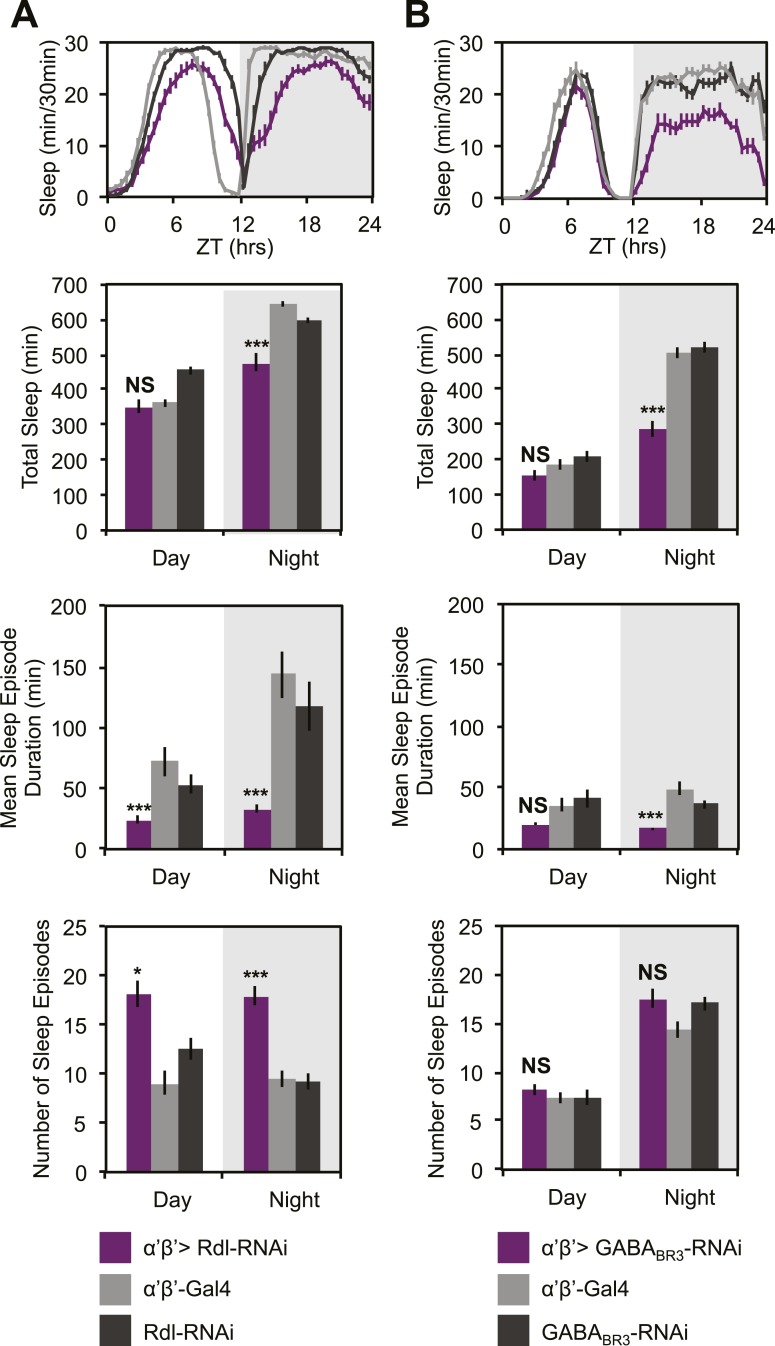
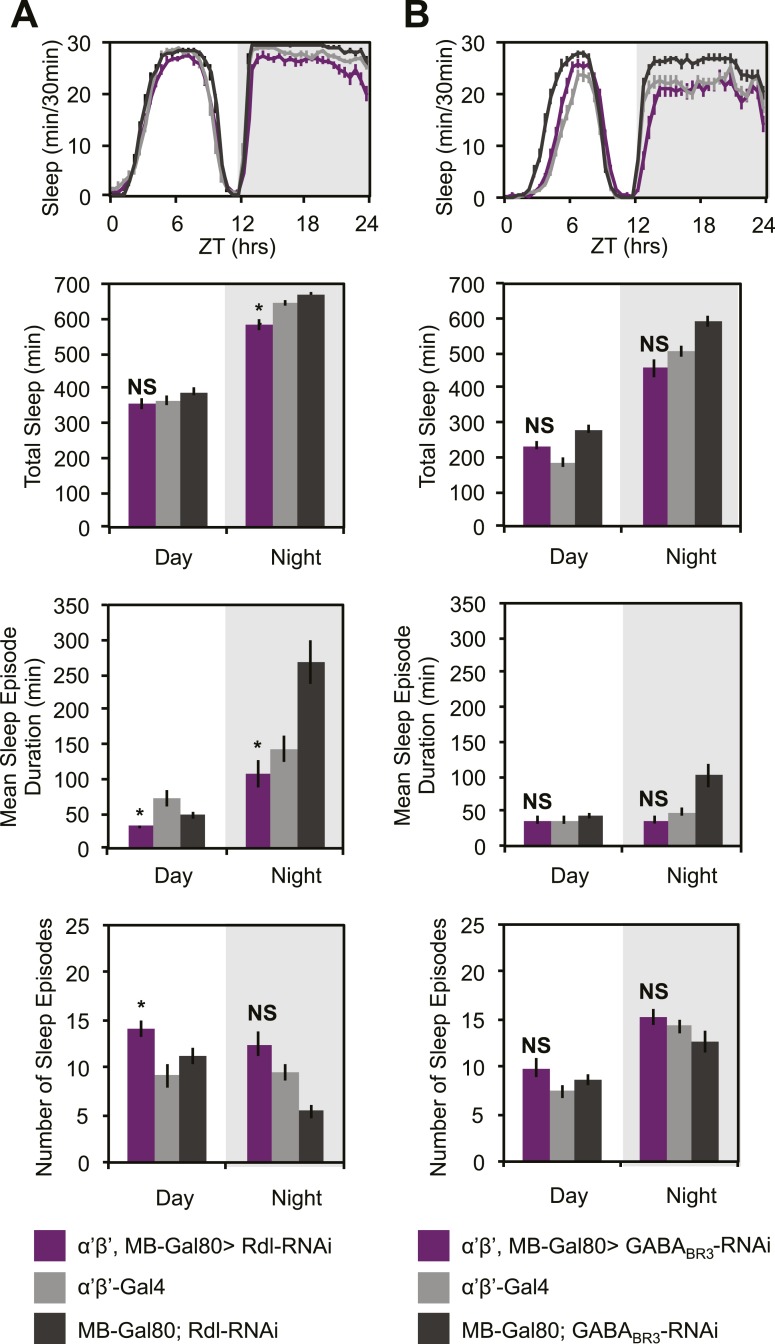
Figure 7. MB α’β’ GABA receptors promote nighttime sleep.
c305a-GAL4 was used to drive expression of Rdl-RNAi (A) or GABABR3-RNAi (B) in the α’β’ neurons. Top: shows total sleep in 30-min bins averaged across 3 days. Middle and bottom plots: show 3-day means of total sleep, mean sleep episode duration and number of sleep episodes quantified in 12-hr day/night bins. α’β’>Rdl-RNAi causes mild sleep loss and increases in nighttime sleep fragmentation, whereas α’β’>GABABR3-RNAi causes greater reductions in total sleep due to a decrease in the average sleep episode length. Grey shading indicates the dark period/night. All data are presented as mean ± SEM where * represents p < 0.05, **p < 0.001 and ***p < 0.0001 using the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon rank sum test. Statistics are described in the ‘Materials and methods’ section.