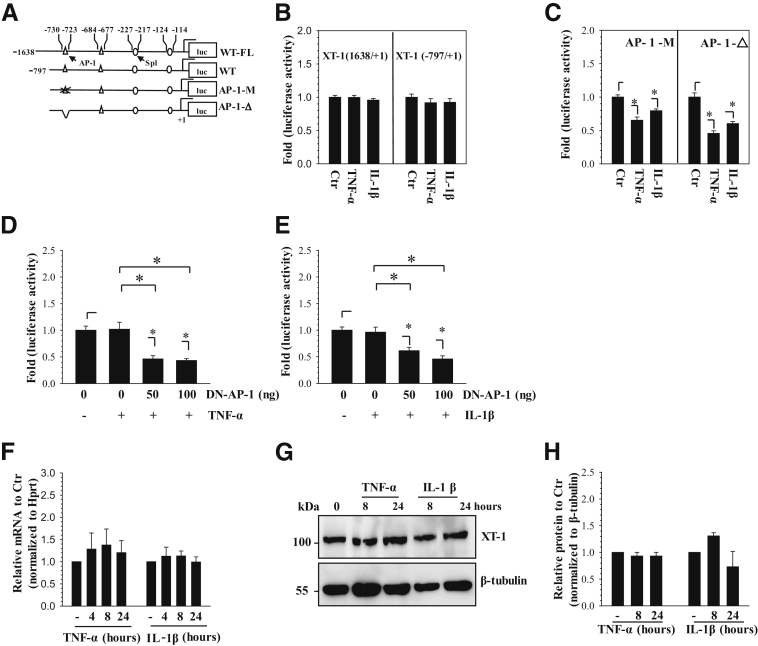
Figure 2.
Xylosyltransferase-1 (XT-1) expression in nucleus pulposus (NP) cells is refractory to inhibition by tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and IL-1β and is maintained through AP-1 signaling. A: Schematic of −1638/+1 bp and −797/+1 bp human XT-1 promoter constructs showing AP-1 and Sp1 binding sites used for the studies. B and C: Rat NP cells transfected with both wild-type XT-1 promoter constructs showed no change in promoter activity in response to TNF-α and IL-1β treatment (B). NP cells transfected with the −797/+1 bp construct harboring either mutation (B) or deletion (C) of the −730/−723 bp AP-1 site showed a decrease in activity in response to cytokines. D and E: NP cells were cotransfected with DN-AP-1 and the −797/+1 bp XT-1 promoter construct and were treated with either TNF-α (D) or IL-1β (E). The XT-1 promoter showed no change in activity in response to cytokines alone; however, activity declined after cytokine treatment in the presence of DN-AP-1. F–H: Quantitative PCR (F) and Western blot (G) and corresponding densitometric (H) analyses of NP cells treated with TNF-α or IL-1β until 24 hours. Cytokine treatment showed no significant change in XT-1 mRNA (F) and protein (G and H) levels. Data represent means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. ∗P < 0.05. Ctr, control; luc, luciferase; WT, wild type; WT-FL, wild type-full length.