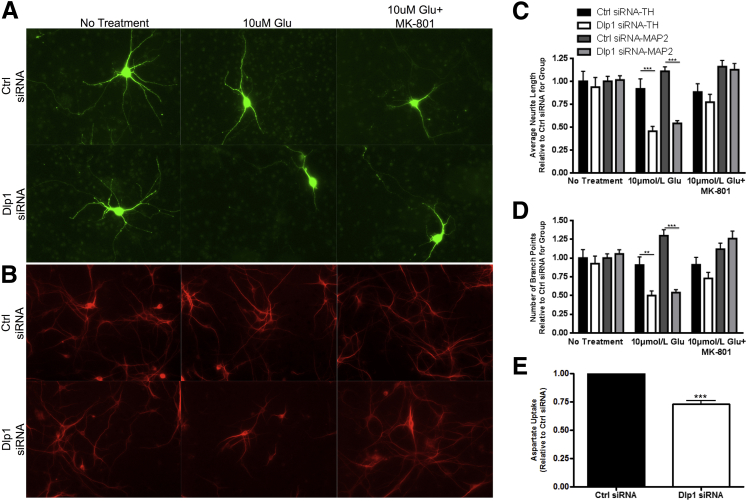
Figure 6.
Astrocytic dynamin-like protein 1 (Dlp1) decreases the ability of astrocytes to protect neurons against the effects of excess glutamate. A: Representative images of dopaminergic (DAergic) neurons, indicated by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) staining, co-cultured with astrocytes transfected with control (ctrl) or Dlp1 siRNA and treated as indicated. Neurons cultured with Dlp1-transfected astrocytes show shorter processes and fewer branch points after glutamate treatment. B: Representative images of non-DAergic neurons, indicated by mitogen-activated protein (MAP) 2 staining, cultured with astrocytes transfected and treated similar to A. C: Average neurite length for images in A and B (n = 3 replicates, 72 to 101 cells per group for TH-positive and approximately 650 to 800 cells per group for MAP2). D: Average number of branch points for images in A and B (n = 3 replicates). Neurite lengths and number of branch points were normalized to the average value for the No Treatment ctrl siRNA group for each replicate, and each value was used for analysis. E: Aspartate uptake decreases in cultures similar to A and D when astrocyte Dlp1 decreases. Data are presented as means ± SEM. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 by two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction (C and D); ∗∗∗P < 0.001 by two-sided unpaired t-test (E).