Abstract
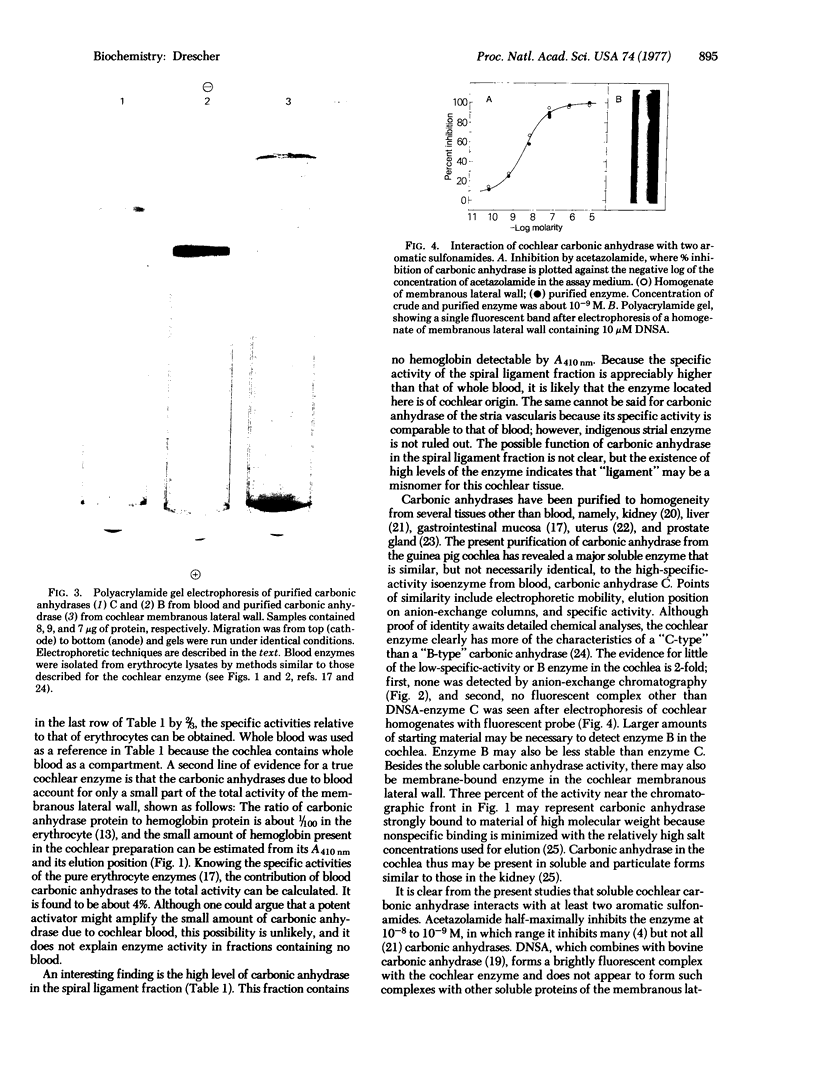
A soluble carbonic anhydrase (carbonate hydro-lyase, EC 4.2.1.1) has been purified to homogeneity from the membranous lateral wall (stria vascularis, spiral ligament, spiral prominence, and outer sulcus) of the guinea-pig inner ear. About 1% of the protein of the membranous lateral wall is carbonic anhydrase. The specific activity of the enzyme in homogenates of the lateral wall is 1.6-1.8 times that of whole blood; for homogenates of the components, stria vascularis and the fraction containing the spiral ligament, the specific activities are 0.9 and 2.0 times the specific activity of whole blood, respectively. No other cochlear fraction examined contains appreciable carbonic anhydrase. The purified enzyme has a molecular weight of about 30,000, a specific activity 60--80% that of carbonic anhydrase C from blood, and an electrophoretic mobility similar to that of the blood enzyme. Cochlear carbonic anhydrase is half-maximally inhibited by 4 X 10(-9) M acetazolamide, is completely inhibited above 10(-5)M acetazolamide, and forms a fluorescent complex with 5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1-sulfonamide, by which it can be distinguished on polyacrylamide gels. This report describes both another isolation of a carbonic anhydrase from a source other than blood and the isolation of an inner-ear enzyme.
Full text
PDF
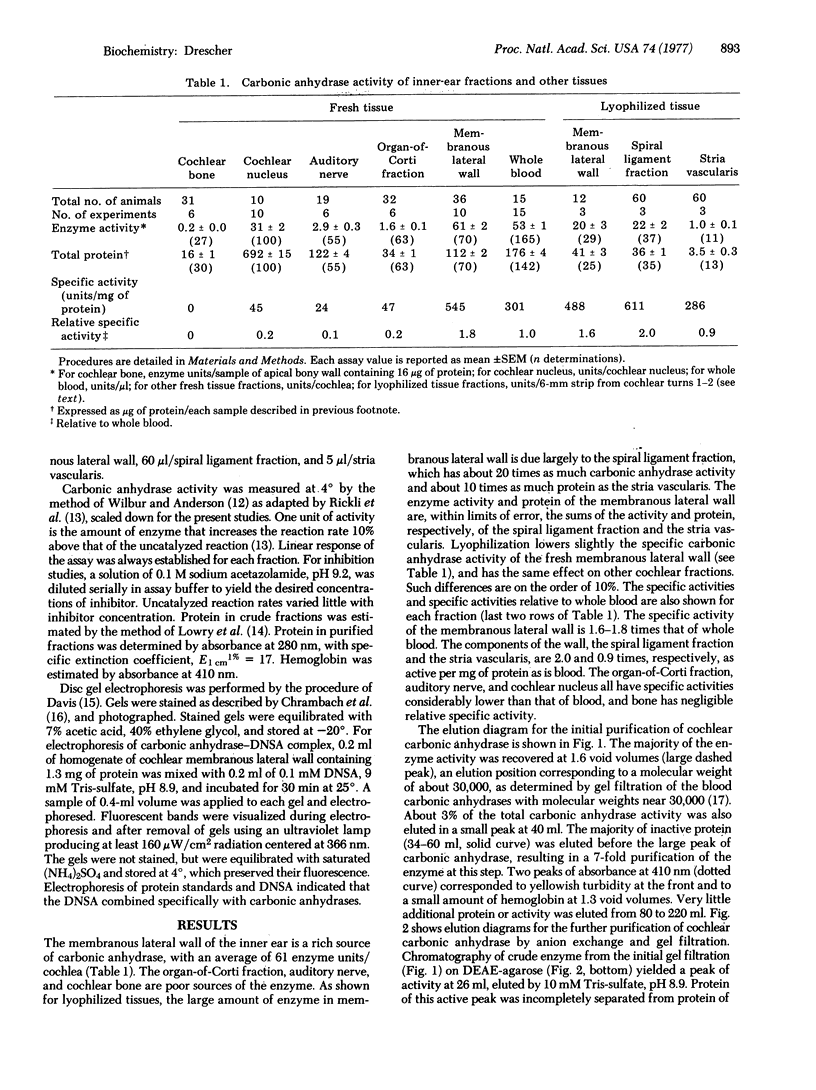
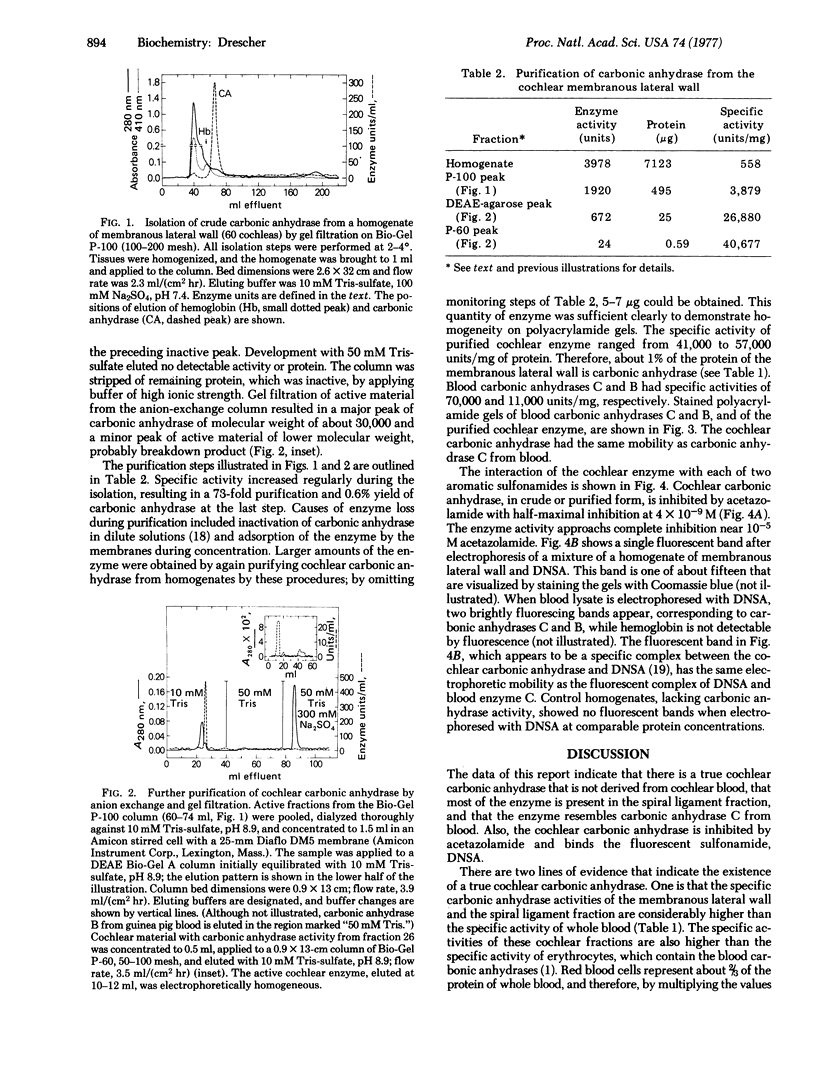

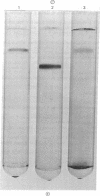
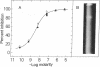
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brusilow S. W., Gordes E. The mutual independence of the endolymphatic potential and the concentrations of sodium and potassium in endolymph. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2517–2521. doi: 10.1172/JCI107442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Parsons D. S. The purification and properties of carbonic anhydrases from guinea-pig erythrocytes and mucosae of the gastrointestinal tract. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):797–808. doi: 10.1042/bj1200797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F., Kernohan J. C. Combination of bovine carbonic anhydrase with a fluorescent sulfonamide. J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 25;242(24):5813–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERULKAR S. D., MAREN T. H. Carbonic anhydrase and the inner ear. Nature. 1961 Feb 11;189:459–460. doi: 10.1038/189459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex J., Wenthold R. J. Choline acetyltransferase, glutamate decarboxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase in the cochlea and cochlear nucleus of the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1976 Jun 18;109(3):575–585. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J. Purification and properties of horse erythrocyte carbonic anhydrases. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 25;243(18):4832–4841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS B. H., EDSALL J. T. KINETIC STUDIES OF HUMAN CARBONIC ANHYDRASES B AND C. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2539–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. W., Garg L. C., Huckson J., Maren T. H. The isolation and partial characterization of sulfonamide-resistant carbonic anhydrases from the liver of the male rat. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Mar;10(2):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuijpers W., Van der Vleuten A. C., Bonting S. L. Cochlear function and sodium and potassium activated adenosine triphosphatase. Science. 1967 Aug 25;157(3791):949–950. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3791.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maren T. H. Carbonic anhydrase: chemistry, physiology, and inhibition. Physiol Rev. 1967 Oct;47(4):595–781. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maren T. H., Swenson E. R., Addink A. D. Rates of ion movement from plasma to endolymph in the dogfish. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1975 Nov-Dec;84(6):847–858. doi: 10.1177/000348947508400618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. E. Carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in the erythrocytes and dorsolateral prostate of the rat. Biochem J. 1969 Sep;114(3):463–476. doi: 10.1042/bj1140463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. E. Carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in the erythrocytes and uterus of the rabbit. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):299–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1200299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley D. N., Whitney P. L. Particulate carbonic anhydrase in homogenates of human kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 11;445(3):780–790. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTS R. F. Acid-base regulation by the kidneys. Am J Med. 1950 Sep;9(3):356–372. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90431-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICKLI E. E., GHAZANFAR S. A., GIBBONS B. H., EDSALL J. T. CARBONIC ANHYDRASES FROM HUMAN ERYTHROCYTES. PREPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF TWO ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Apr;239:1065–1078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. A., LOWRY O. H., WU M. L. The electrolytes of the labyrinthine fluids. Laryngoscope. 1954 Mar;64(3):141–153. doi: 10.1288/00005537-195403000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein H., Yules R. B. The effect of diuretics on cochlear potentials and inner ear fluids. Laryngoscope. 1971 Jun;81(6):873–888. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197106000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wistrand J., Lindahl S., Wåhlstrand T. Human renal carbonic anhydrase. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):189–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]