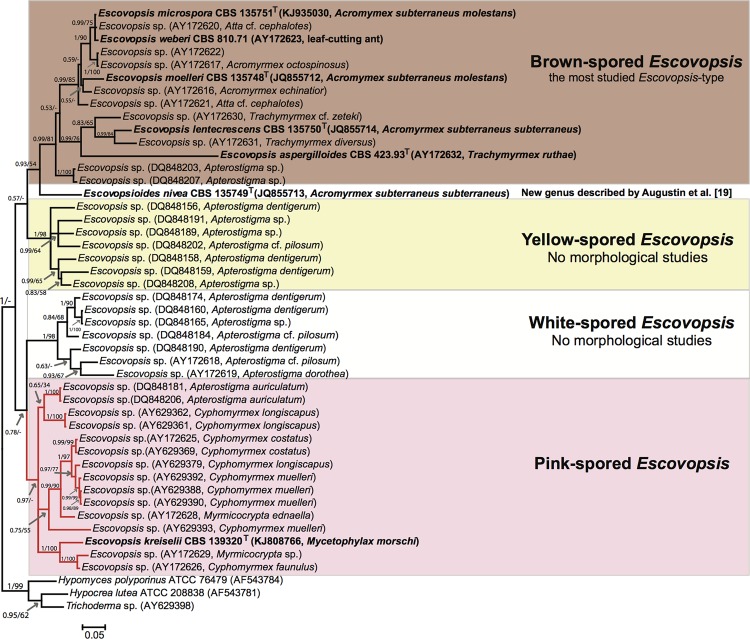
Figure 3. Phylogenetic position of Escovopsis kreiselii within the Escovopsis clade based on tef1 sequences reconstructed using Bayesian Inference.
All Escovopsis species described so far are denoted in bold. In addition to the newly described species, forty-three tef1 sequences representing all Escovopsis morphotypes used in previous studies were retrieved from GenBank. Sequences of tef1 from other Hypocreaceae were used as outgroup. The voucher accession numbers in culture collections follow the taxon names. GenBank accessions and the ant species from which the fungi were isolated are given in parentheses. Different colors indicate the fungal morphotypes found in the Escovopsis clade. Bootstrap values from ML analyses are also indicated from a similar topology. Only PP and bootstrap values ≥ 0.5 or 50 are shown. Phylogeny based on Gerardo et al. [9]. T: ex-type strains. Bar: 0.05 substitutions per nucleotide position.