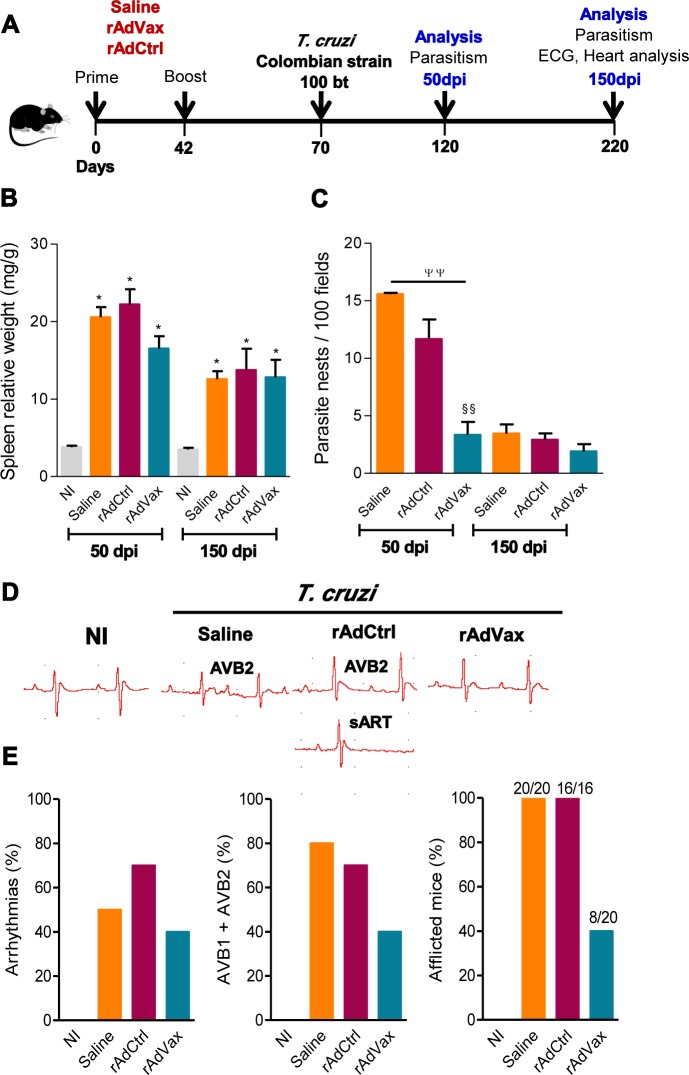
Figure 1. Heart parasitism and electrical abnormalities are reduced in rAdVax-vaccinated mice challenged with the Colombian strain.
(A) Mice were primed-boosted (s.c.) with 2 × 108 plaque-forming units (PFU) of rAdCtrl or a mixture of 108 PFU of each recombinant adenovirus vaccine construction (rAdASP2+rAdTS; rAdVax) or the vehicle control saline at 6-week intervals. Four weeks after the last immunization, the mice were challenged (i.p.) with 100 blood trypomastigotes (bt) of the Colombian T. cruzi Type I strain and analyzed during the acute (50 dpi) and chronic (150 dpi) phases of infection. (B) Relative spleen weight (mg of spleen/g of body). (C) Quantitative immunohistochemical staining data for T. cruzi parasitism (nests/100 microscopic fields) in the heart tissue. (D) Representative electrocardiogram (ECG) register segments of sex- and age-matched noninfected (NI) controls and mice injected with saline, rAdCtrl or rAdVax, challenged with T. cruzi and analyzed at 150 dpi. (E) Summary of the group data from NI controls and saline-injected, rAdCtrl- or rAdVax-immunized and T. cruzi-infected mice showing the frequency of mice presenting arrhythmias (ART), second-degree atrioventricular block (AVB2) and afflicted with ECG alterations, at 150 dpi. The data are presented as the means ± SD of seven to ten mice per group. *P <0.05, experimental groups compared with NI controls. ΨΨ P < 0.01, rAdVax-immunized compared with saline-injected T. cruzi-infected mice. §§ P < 0.01, rAdVax-immunized compared with rAdCtrl-injected T. cruzi-infected mice.