Figure 5.
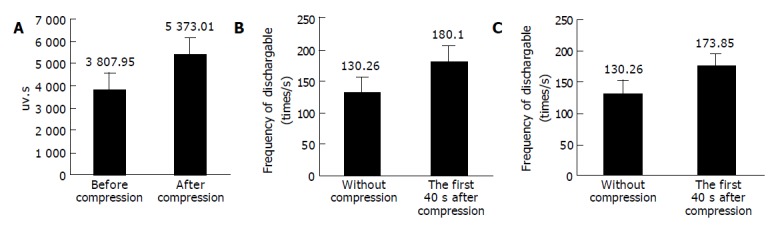
Comparison of electric discharge of vagus nerve. A: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve through analyzing the absolute value of an area of wave form before and after the compression (from 4 to 40 s under the intracranial hypertension), and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension, n = 20, P<0.05; B: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve before and during the first 4 s after the rabbit’s lateral ventricle compression. We analyzed the electric discharge frequency of the dischargeable wave in each time segment by setting a single liminal value line, and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension; C: The comparison of the electric discharge of vagus nerve before the compression and during continuous compression (from 4 to 40 s). We analyzed the electric discharge frequency of the dischargeable wave in each time segment by setting a single liminal value line, and the neural discharge of vagus nerve had increased after intracranial hypertension.
