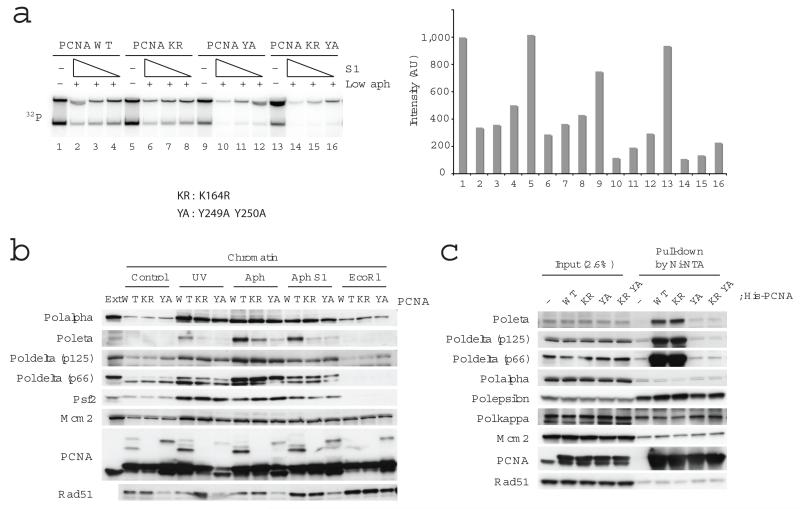
Figure 5.
The role of PCNA in DNA replication and chromatin association of replication proteins upon fork collapse. In (a) replication of sperm nuclei incubated in extracts for 80 min in the presence of 1 μg ml−1 aphidicolin and 0, 0.73, 0.37, 0.18 U μl−1 S1 nuclease and PCNA wild type (WT), PCNA K164R (KR), PCNA Y249A Y250A (YA) or PCNA K164R Y249A Y250A (KR YA) recombinant proteins. Replication products were resolved by neutral agarose gel and subjected to autoradiography (left). Signal intensities were quantified and reported in the graph (right). (b) Binding to chromatin of the indicated proteins was monitored by immunoblotting of chromatin treated with 200 J m−2 UV or incubated in extracts treated with 1 μg ml−1 aphidicolin, 0.97 U μl−1 S1 nuclease or 0.1 U μl−1 EcoR1 and recombinant PCNA wild type (WT), PCNA K164R (KR) or PCNA Y249A Y250A (YA) as indicated. 0.5 μl egg extract was loaded as a control (Ext). (c) The interaction of PCNA and replication proteins in egg extract was monitored by incubation of His-tagged wild type and mutant PCNA proteins followed by pull down with Ni-NTA sepharose. The interacting proteins were detected by immunoblotting as indicated.