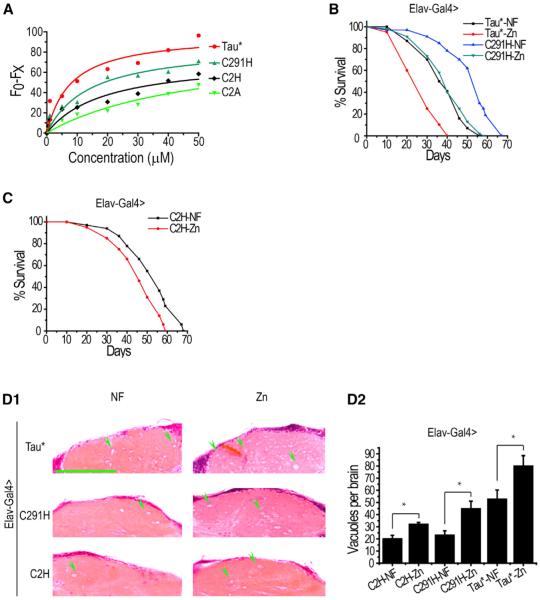
Figure 6. Restoration of Zinc Binding to Tau Regains Correlatively Its Zinc Responsiveness.
(A) Various forms of Tau* upon zinc binding as detected by intrinsic fluorescence quenching. Fluorescence excited at 280 nm was measured after 5 min equilibration.
(B) Lifespan of Tau*C291H flies versus zinc. Zinc supplementation can enhance Tau*C291H toxicity to a level approaching that of Tau under normal diets. Elav-Gal4 was used to drive Tau expression. Tau*-NF versus Tau*-Zn, p < 0.0001; Tau*C291H-NF versus Tau*C291H-Zn, p < 0.0001.
(C) Lifespan of Tau*C2H flies. Comparing with that of Tau*C2A, the lifespan of Tau*C2H flies can still be affected by zinc. Tau*C2H-NF versus Tau*C2H-Zn, p < 0.01.
(D1 and D2) Brain degeneration was also affected by zinc treatment in Tau*C291H and Tau*C2H flies. Shown here are H&E-stained paraffin brain sections of Tau*, Tau*C291H, and Tau*C2H flies under zinc treatment. A quantitative and statistical analysis is shown in D2. The scale bar represents 50 μm. Green arrowheads indicate only some of the many degenerated vacuoles. Data represent mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.