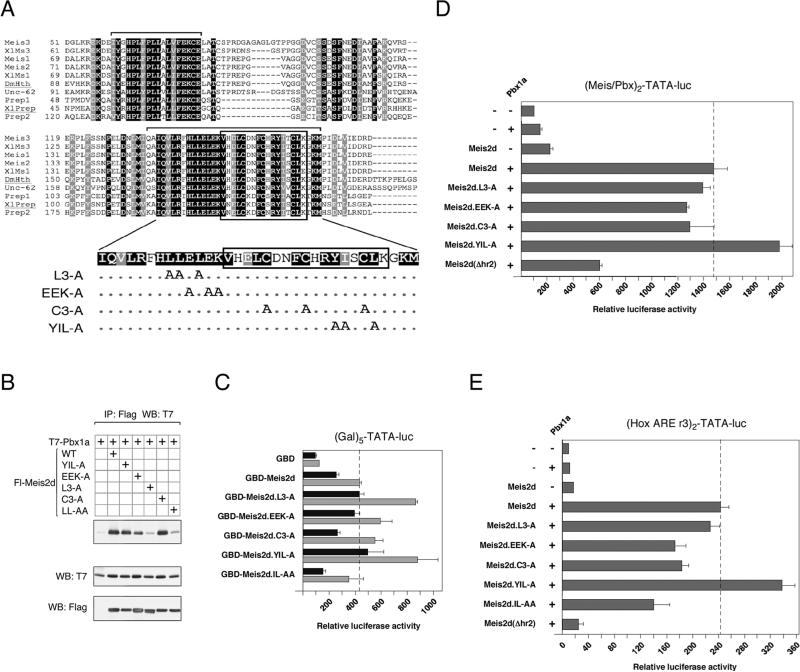
Fig. 6.
Mutational analysis of hr2. A) An alignment of the Hth domains from Meis relatives is shown. Amino acids which are identical or similar between all sequences shown are shaded black and gray respectively. The sequences shown are Meis1, Meis2, Meis3, Prep1 and Prep2 from human, Xenopus laevis Meis1, Meis3 and Prep (XlMs1, XlMs3 and XlPrep), the Drosophila melanogaster HTH protein (DmHth) and a Meis-like protein from C. elegans (Unc-62). Brackets above the sequences indicate the hr1 and hr2 regions. Mutations within the Meis2 hr2 are shown below. Dots indicate no change. B) COS1 cells were transfected with the indicated Flag-tagged Meis2 expression constructs and T7-Pbx1a. Proteins were isolated on Flag agarose and the presence of coprecipitating Pbx1a analyzed by T7 western blot. Expression in the lysates is shown below. C) Two amounts of each of the indicated GBD-Meis2d fusions were cotransfected into HepG2 cells with the (Gal)5-TATA luciferase reporter, and luciferase activity was assayed after 48 hours. The dashed line indicates the maximum activation level by Meis2d. HepG2 cells were transfected with the indicated Meis2d, Pbx1a and HoxB1 expression constructs together with the Meis/Pbx reporter (D) or Hox ARE reporter (E), and luciferase activity was determine after 48 hours. The dashed lines indicate activity with wild type Meis2d.