Figure 4.
Structural Changes at the Coils/Hinge Junction upon DNA and ATP Binding
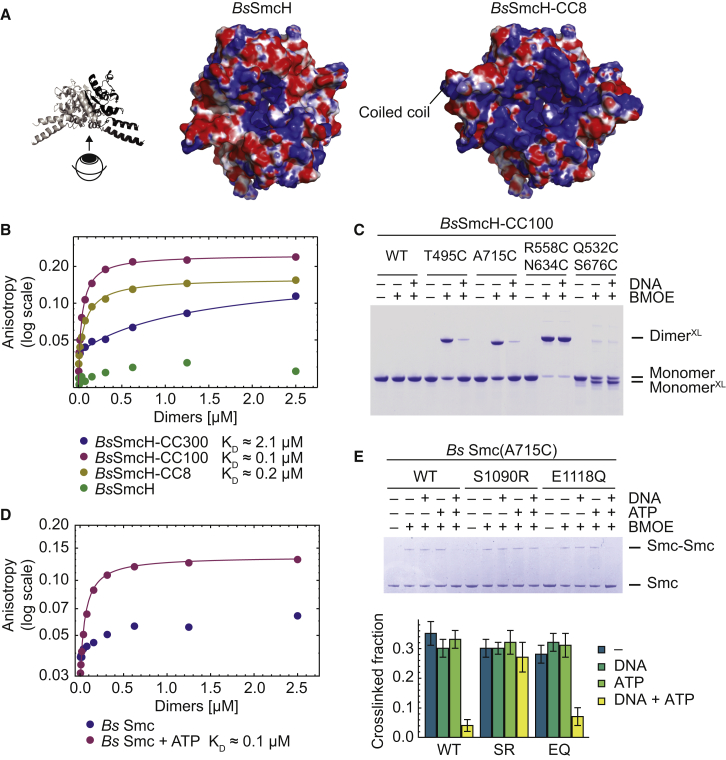
(A) Bottom view of electrostatic surface potential maps of Bs Smc hinge models (Kurze et al., 2011) based on the Tm Smc hinge structure (PDB ID: 1GXL). Left: isolated Bs Smc hinge. Right: hinge with short coiled coils.
(B) DNA binding of Bs Smc fragments measured by fluorescence anisotropy using fluorescein-labeled DNA (40 bp).
(C) Crosslinking of cysteine-bearing variants of BsSmcH-CC100 with and without DNA. XL denotes species crosslinked by BMOE. WT, wild-type.
(D) DNA binding of Bs Smc in the presence and absence of ATP measured by anisotropy using fluorescein-labeled DNA (40 bp).
(E) Crosslinking of Bs Smc(A715C) variants with and without mutations in the ABC signature and Walker B motif (S1090R [SR] and E1118Q [EQ], respectively). The four endogenous cysteines have been replaced by serines. Quantification of crosslinking efficiency is based on three independent replicates. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S3.