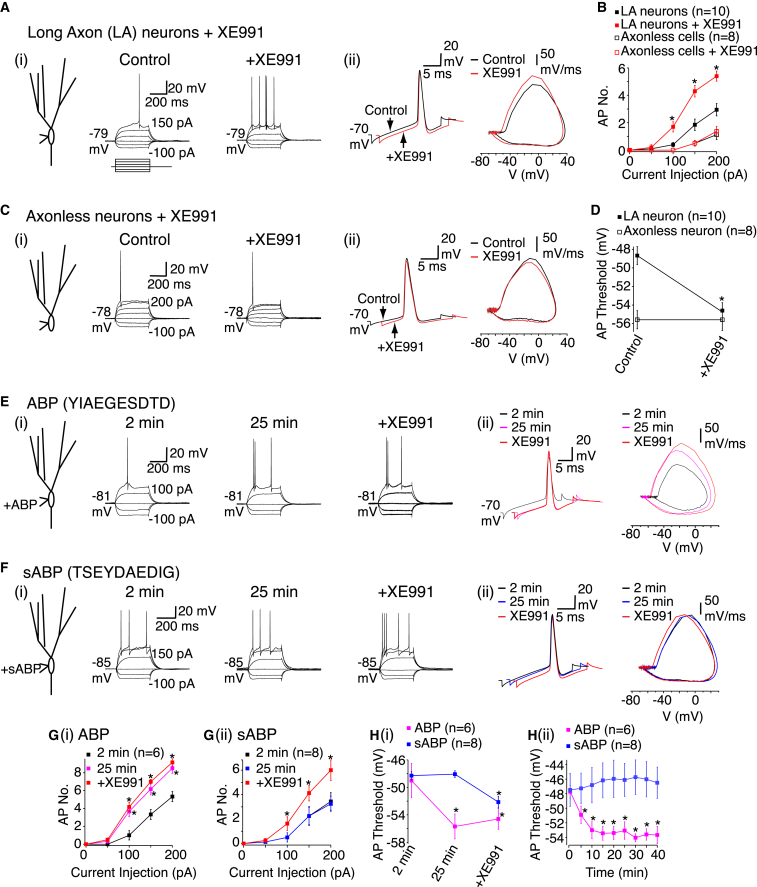
Figure 3.
Axonal KV7 Channels Regulate the Action Potential Threshold
(Ai and Ci) Example records from long axon (LA) and axonless granule cells in the absence and presence of XE991 (3 μM). The RMP values are adjacent to the traces. The scale shown applies to both traces in the panel.
(Aii and Cii) Typical spikes and phase plane plots before (black) and after (red) XE991 treatment in LA and axonless neurons.
(B and D) Average spike numbers (AP No.) in response to 400 ms current pulses and mean spike threshold under control conditions and following XE991 treatment in LA and axonless neurons, respectively.
(Ei and Fi) Representative traces and RMP values (adjacent to the traces) when either ABP (8 mM) or scrambled ABP (sABP, 8 mM) were included in the patch pipette for 2 min (control) and 25 min. XE991 was subsequently applied. The scale shown applies to all traces in the panel.
(Eii and Fii) Action potentials at 2 min, 25 min, and after XE991 treatment when ABP and sABP were incorporated in the intracellular solution, respectively.
(G and Gii) Average spike numbers generated with varying 400 ms current pulses 2 min and 25 min after ABP/sABP dialysis and following XE991 treatment.
(Hi) Average spike threshold 2 min, 25 min, and after XE991 with ABP or sABP.
(Hii) The action potential threshold time course with ABP or sABP.