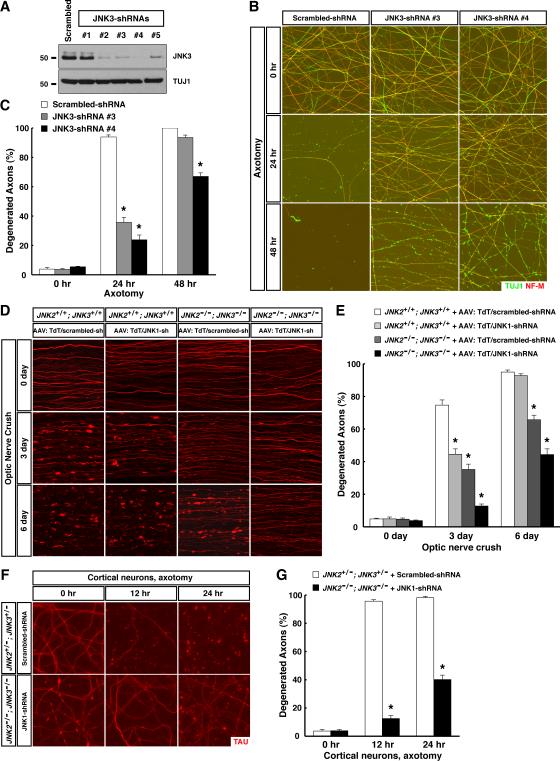
Figure 3. JNK1 and JNK3 function as the predominant MAPKs assisted by JNK2 in axon degeneration after traumatic injury. See also Figure S4 and Table S1.
(A to C) JNK3 regulates degeneration of injured sensory axons. Cultures of embryonic DRG neurons were subjected to lentiviral-shRNA knockdown of JNK3. Efficiency of lentiviral-shRNAs was examined by immunoblot analysis of axonal proteins harvested from each condition (A). Degeneration of axons transduced with the two most efficient lentiviral-shRNAs was visualized by immunostaining at indicated time points after axotomy (B), and degeneration was quantified (C), n=3 for each condition. (D and E) JNK1 and JNK3 function as the predominant MAPKs in regulating degeneration of injured RGC axons in vivo. RGCs of the mice with indicated genotypes were transduced with TdTomato/scrambled-shRNA or TdTomato/JNK1-shRNA virus. Degeneration of TdTomato-positive axons was visualized at indicated time points after optic nerve crush (D), and degeneration was quantified (E), n=4 for each condition. (F and G) JNK1 / JNK2 / JNK3 regulate degeneration of injured cortical axons. Cultures of embryonic cortical neurons with indicated genotypes were transduced with lentivirus expressing scrambled-shRNA or JNK1-shRNA. Axon degeneration at indicated time points following axotomy was visualized by immunostaining (F), and degeneration was quantified (G), n=3 for each condition. Values are presented as mean ± SEM; *, p < 0.01.