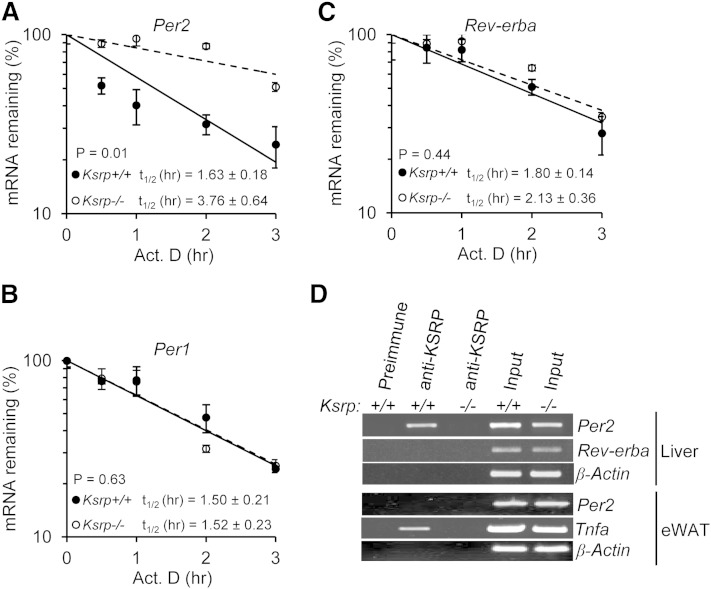
Fig. 6.
KSRP controls Per2 mRNA stability through a direct RNA-protein interaction. A, B, and C: Half-lives of Per2 mRNA (A), Per1 mRNA (B), and Rev-erba mRNA (C) in wild-type and Ksrp−/− hepatocytes. Hepatocytes were treated with actinomycin D (Act. D), and RNA was isolated at different time points after the treatment. mRNA levels of Per2, Per1, and Rev-erba were analyzed by qPCR. The mRNA decay rates were plotted, and the half-lives (t1/2) were indicated. Each time point represents mean ± SEM (n = 3). D: Association of Per2 mRNA with KSRP. Liver extracts were prepared from wild-type and Ksrp−/− mice and subjected to immunoprecipitation with preimmune serum or anti-KSRP serum. RNA was isolated from the precipitation. The presence of Per2, Rev-erba, and β-Actin mRNAs was analyzed by RT-PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis. eWAT extracts were also prepared from wild-type and Ksrp−/− mice and subjected to immunoprecipitation with preimmune serum or anti-KSRP serum. The presence of Per2, Tnfa, and β-Actin mRNAs in the immunoprecipitates was analyzed. Input: RT-PCR reaction of RNA (10% of amounts used for IP) from each genotype.