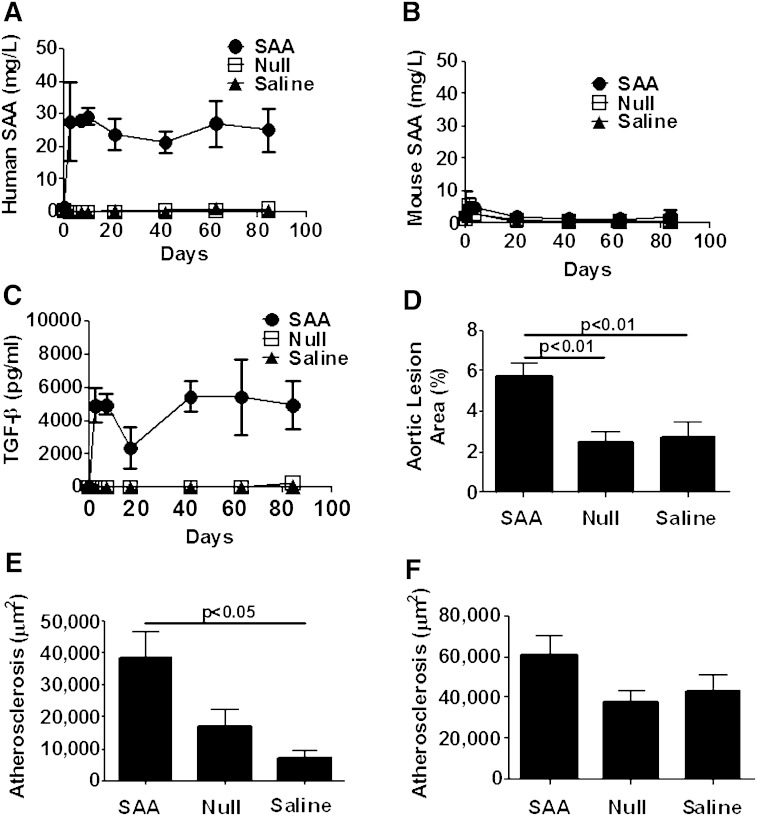
Fig. 5.
Atherosclerosis was increased after sustained elevation of human SAA in rag1−/− × apoe−/− mice. Mice were injected with ad-SAA (black circles), ad-Null (open squares), or saline (black triangles) every 21 days and fed normal rodent chow for 12 weeks. A: Mice receiving ad-SAA had a significant, persistent elevation of human SAA. B: Murine SAA did not increase nor did it differ between groups throughout the study. C: TGF-β was increased only in mice injected with ad-SAA and remained elevated throughout the study. Shown are means ± SEM from n = 2–6 mice/group per time point. Ad-SAA-injected mice had increased atherosclerosis on the aortic intimal surface (D) and in the brachiocephalic artery (E). There was a trend toward increased atherosclerosis in the aortic root that did not reach significance (F). Data are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 4–16/group analyzed by one-way ANOVA.