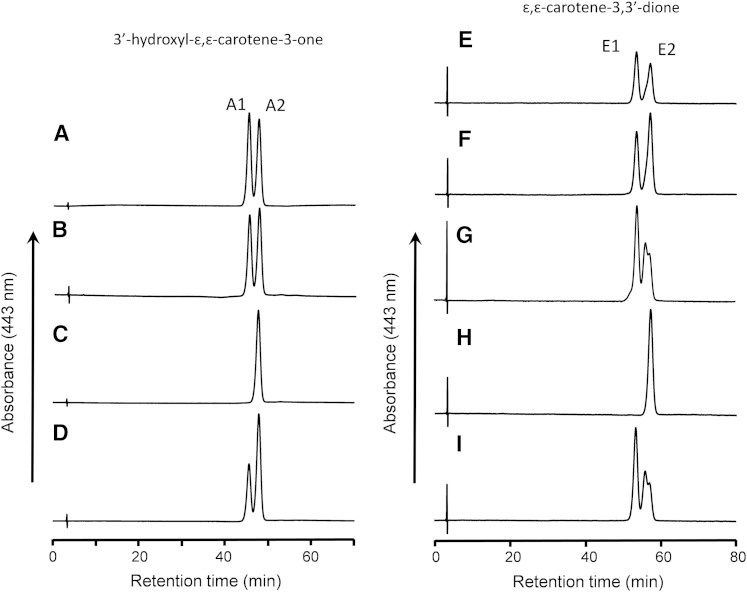
Fig. 3.
HPLC profiles of 3′-hydroxy-ε,ε-caroten-3-one (A–D) and ε,ε-carotene-3,3′-dione (E–I) isolated from different sources on a chiral column. A, E: Incubation mixture of lutein with postmitochondrial fraction of mouse liver. B, F: Liver extract of mice fed lutein. C: 3′-Hydroxy-ε,ε-caroten-3-one prepared from lactucaxanthin. D: A mixture of (A) and (C). G: Incubation mixture of zeaxanthin with postmitochondrial fraction. H: ε,ε-Carotene-3,3′-dione prepared from lactucaxanthin. I: Egg yolk. Peak A1, (6S,3′R,6′R)-3′-hydroxy-ε,ε-caroten-3-one; peak A2, (6R,3′R,6′R)-3′-hydroxy-ε,ε-caroten-3-one; peak E1, meso-ε,ε-carotene-3,3′-dione; peak E2, (6R,6′R)-ε,ε-carotene-3,3′-dione.