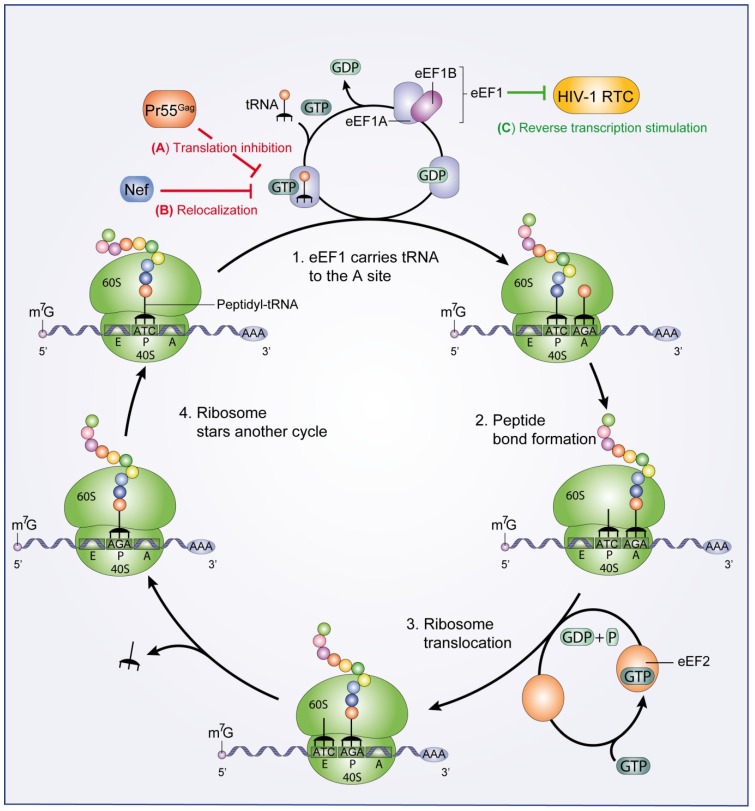
Figure 2.
Eukaryotic translation elongation. eEF1A-GTP transports the aminoacylated tRNAs into the A site of the 80S ribosome and eEF1A-GDP is re-activated by eEF1B (step 1). The 80S ribosome-mediated peptide bond formation (step 2) precedes ribosome translocation mediated by eEF2 (step 3). Finally, the ribosome begins another cycle of peptide elongation (step 4). HIV-1 viral functions important to control the eukaryotic translation elongation are shown. (A) HIV-1 Pr55Gag interacts with eEF1A and induces translation inhibition (red line); (B) HIV-1 Nef protein also interacts with eEF1A and mediates a nucleocytoplasmic relocalization of eEF1A (red line); (C) The HIV-1 RTC recruits eEF1 to stimulate late steps of the HIV-1 reverse transcription process (green line).