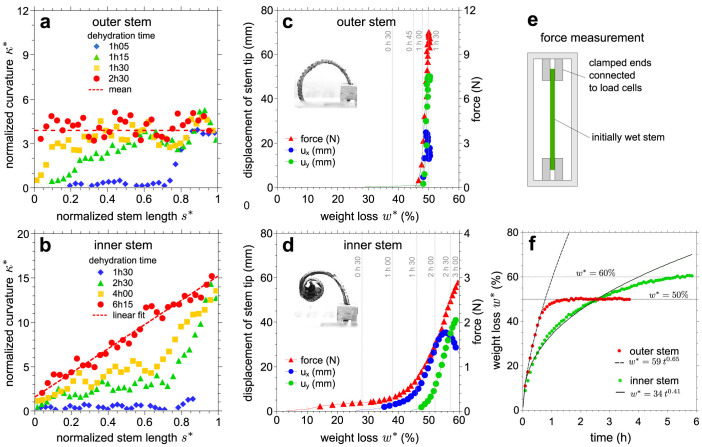
Figure 2. Response of outer and inner stems to dehydration.
The normalized curvature κ* = κl as a function of the normalized arc-length s* = s/l of (a) outer and (b) inner stems of S. lepidophylla at different time intervals. Mechanical response of initially wet stems to dehydration for (c) the outer and (d) the inner stems. Plotted as a function of the weight loss w* of the stem during dehydration, the absolute displacements of the stem tip, ux and uy, and the reaction force of a similar stem clamped at its both ends illustrate that stem curling correlates with induced-stress buildup. The vertical lines in gray represent the associated dehydration time. (e) Force measurement setup. (f) Dehydration weight loss w* of outer and inner stems as a function of time. The early drying behaviour before reaching an equilibrium is fitted with a power-law function.