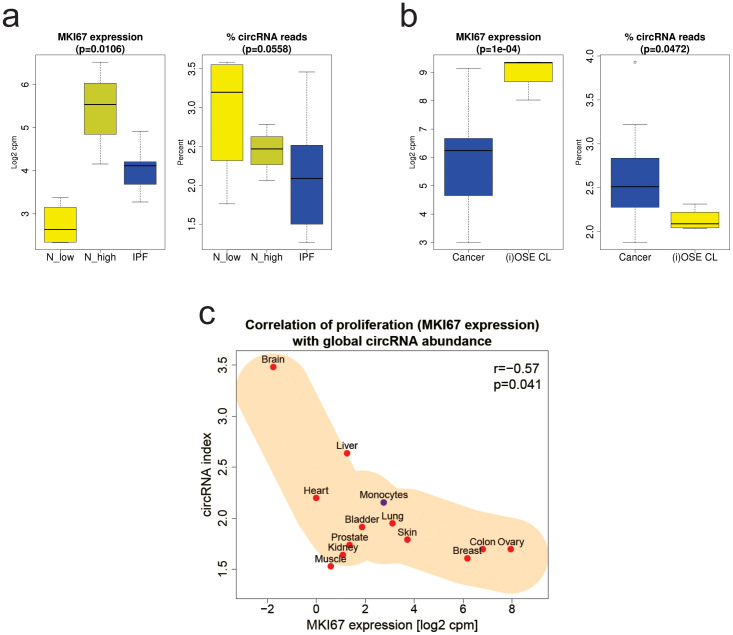
Figure 5. Validation of the correlation of the circRNA index with MKI67 expression.
(a) Normal lung tissues (four with low MKI67 expression, N_low, and three with high MKI67 expression, N_high) and tissues from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a non-cancerous neo-proliferative disease (Supplementary Table 4a) are compared concerning MKI67 expression (p = 0.011, Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test) and percent circRNA reads (trend p-value = 0.056, Kruskal-Wallis rank sum test, R-package compareGroups). (b) Ascitic ovarian cancer cells (Cancer) and (immortalised) normal ovarian surface epithelium cell lines ((i)OSE CL) (Supplementary Table 4b) are compared concerning MKI67 expression (p = 1e-04) and percent circRNA reads (p = 0.047, both Kruskal-Wallis rank sum tests). Yellow indicates normal tissues or cell lines and blue indicates tissues or cells from the diseased state. (c) Correlation of MKI67 expression and global circRNA abundance (the circRNA index) in 13 human tissues (red, twelve human tissues from study SRP033095 and blue, monocytes from study E-MTAB-2399). A significant strong negative correlation (Pearson correlation coefficient ρ = -0.573, p = 0.041) is seen (Supplementary Table 4c).