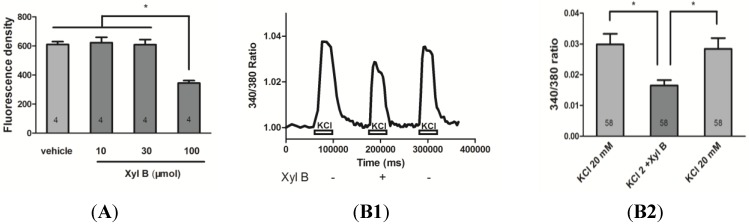
Figure 1.
Neuroprotective effects of xyloketal B in cortical neuronal cell culture in vitro. (A) Xyloketal B reduced OGD-induced primary cortical cell death. Cells were grown in 96-well plates followed by treatment with the indicated concentrations of xyloketal B or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 30 min and then subjected to OGD for 90 min. Cell death was determined using propidium iodide (PI, 1 μg/mL) staining. Fluorescence density of PI was detected with a microplate reader. Xyloketal B (100 μM) significantly decreased fluorescence density as compared to the other groups. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. * indicates p < 0.05, n = 4. (B) Fura-2 ratiometric calcium imaging showing that xyloketal B reduced KCl-induced calcium entry in primary cortical neurons. (B1) Representative and (B2) summary of fura-2 calcium signals in cortical neurons (day in vitro 6, DIV 6) were incubated with vehicle or xyloketal B (100 μM), followed by 20 mM KCl-induced calcium influx detection using fura-2 calcium indicator. Incubation of xyloketal B (100 μM) reduced calcium influx caused by membrane depolarization by 34% ± 9% of the vehicle treatment. *: p < 0.05, n = 58.