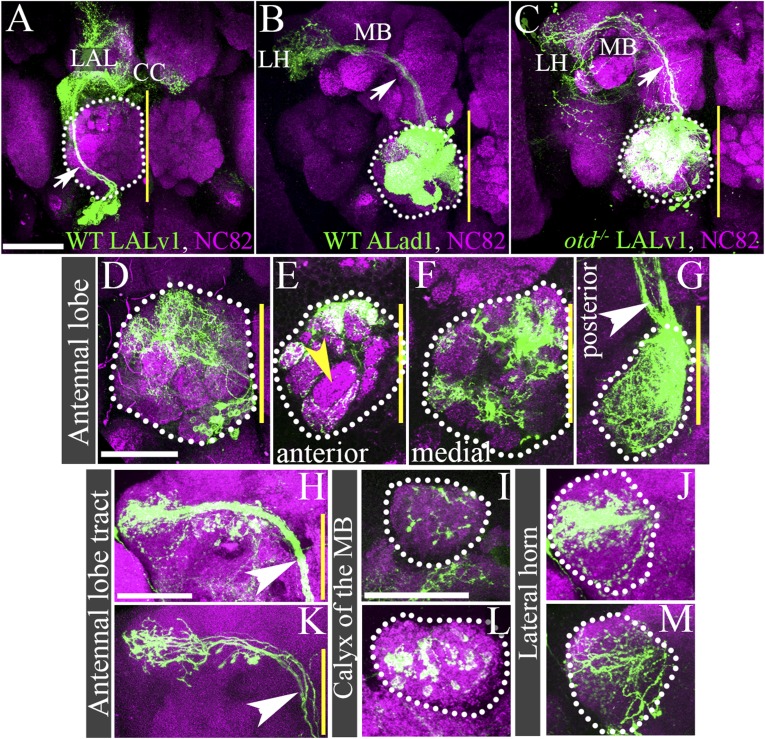
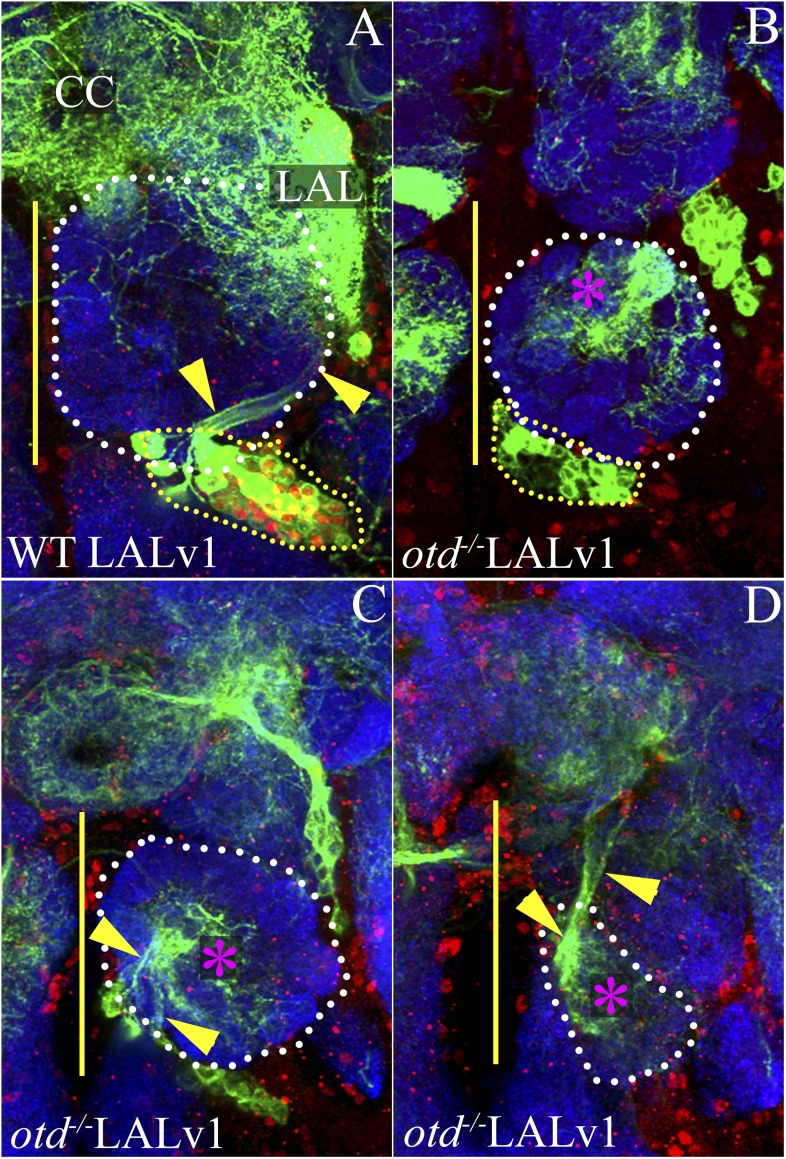
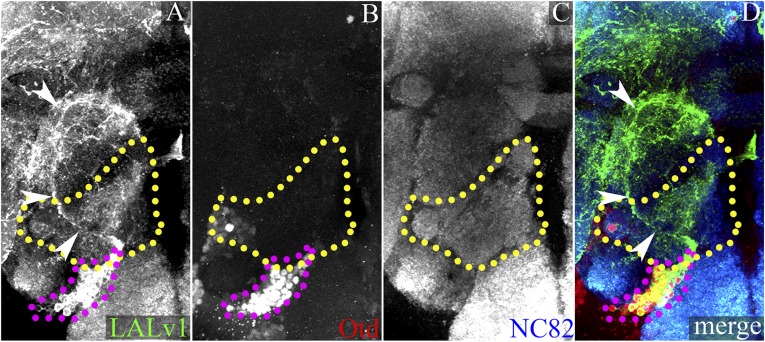
Figure 4. Loss of otd from LALv1 lineage results in activation of the antennal lobe-specific enhancer, GH146-Gal4, thus allowing detailed study of the neuroanatomy of the transformed otd-−/− LALv1 lineage.
(A and B) show WT LALv1 and ALad1 lineages, respectively, and (C) shows an otd−/− LALv1 lineage. Note that the neuroanatomy of the otd−/− LALv1 lineage (C) is completely unlike the WT LALv1 lineage (A) and is strikingly similar to the WT ALad1 lineage (B). (D–M) document different brains that contain the otd−/− LALv1 lineage. They have multiglomerular dendritic innervations in the AL (D–G), but not all glomeruli are always innervated (yellow arrowhead in E). There are more innervations in the more posterior parts of the antennal lobe (F and G). Their axon tracts project via the medial antennal lobe tract (arrowhead in C, G, H, K) to innervate the calyx of the mushroom body (MB; I and L) and the lateral horn (LH; J and M). Genotype in A: FRT19A/FRT19A,Tub-Gal80,hsFLP; Per-Gal4,UAS-mCD8::GFP/+. Genotype in B: FRT19A/FRT19A,Tub-Gal80,hsFLP; GH146-Gal4,UAS-mCD8::GFP/+. Genotype in C–M: FRT19A,oc2 or FRT19A,otdYH13/FRT19A,Tub-Gal80,hsFLP; GH146-Gal4,UAS-mCD8::GFP/+. Scale bars are 50 µm (scale bar in A is applicable to B and C; the one in D is applicable through to G; the one in H is applicable to K; the one in I is applicable to L, J, M). Yellow line represents the midline.