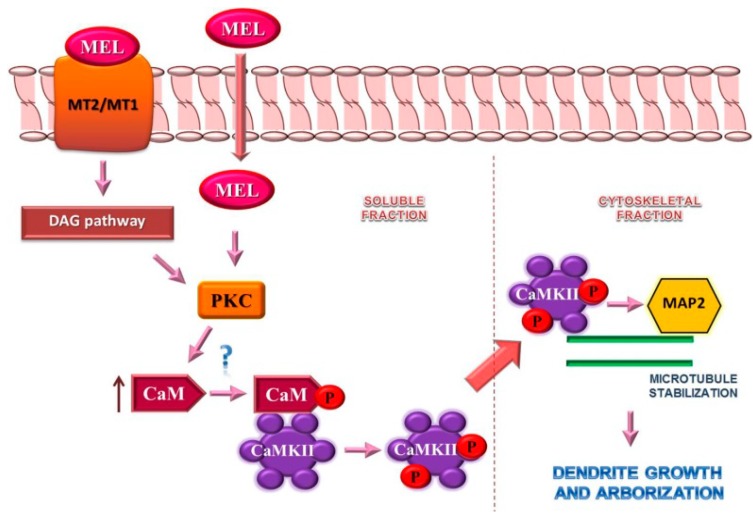
Figure 9.
Schematic drawing of the signaling pathway by which Melatonin stimulates dendrite formation. Melatonin (MEL) binds to membrane receptors (MT2/MT1) to activate PKC through the diacylglycerol (DAG) pathway. Also, the indoleamine can diffuse through the plasmatic membrane to directly interact with protein kinase C (PKC). This enzyme may phosphorylate calmodulin (CaM), which can bind to Ca2+/CaM Kinase II (CaMKII) with higher affinity. CaM-activated CaMKII undergoes autophosphorylation which induces its targeting to the cytoskeletal compartment where it binds and phosphorylates MAP2 to constitute dendrites. Also, PKC may increase CaM levels in the soluble fraction by an enhanced biosynthesis or by targeting from the cytoskeletal to the soluble compartment.