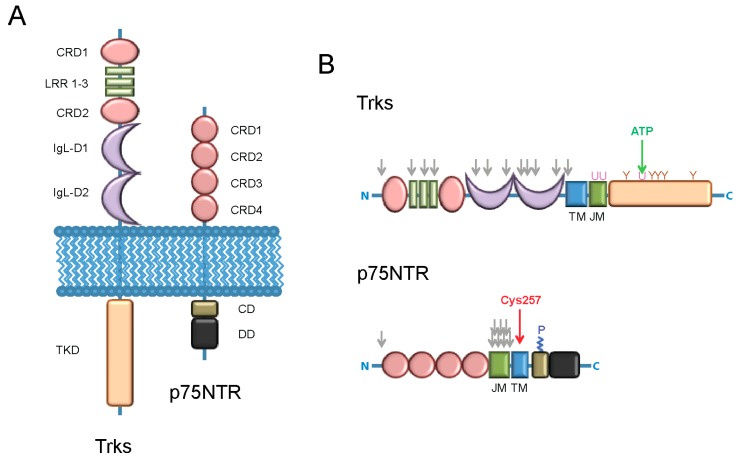
Figure 1.
Schematic picture of tropomyosin receptor kinases (Trks) and the p75 neurotrophin receptors (p75NTR). (A) Structure of the two receptors: The intracellular (on top) and extracellular (on bottom) domains are highlighted. The following abbreviations are used: CRD (cystein-rich domain); LRR (leucine-rich domain); IgL-D (immunoglobulin-like domain); TKD (tyrosine-kinase domain); CD (chopper domain); DD (death domain); (B) Modified residues of the Trks (on top) and of p75NTR (on bottom) receptors. The following abbreviations are used: TM (transmembrane domain); JM (juxta-membrane domain); N (N-terminus); C (C-terminus). The following symbols are used: Grey ↓ (N- or O-glycosylation sites); green ↓ (ATP-binding site); red ↓ (site of covalent homo-dimerization due to the disulfide bond formed by Cys257 [32,33]). U (ubiquitination-related lysine residues, as derived from studies mainly performed on the TrkA receptor [34,35,36,37]); Y (phosphorylated tyrosine residues, their numeration and function is described in Figure 2); P (palmitoylated Cys residue [38]).