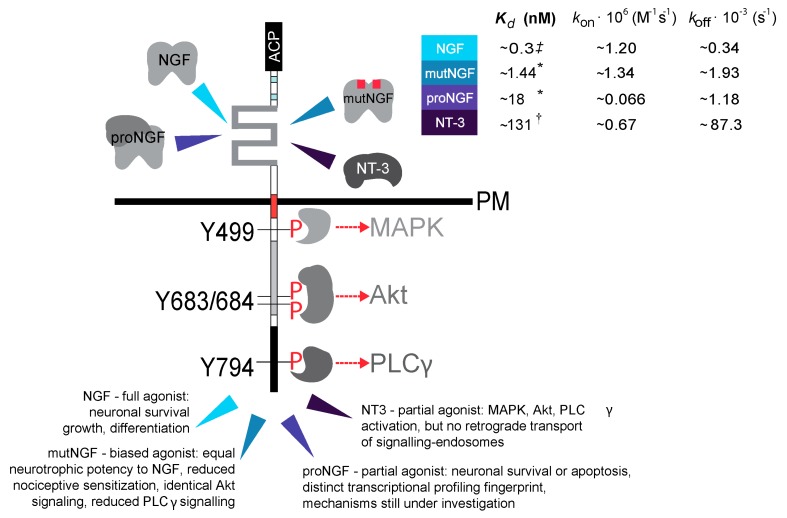
Figure 2.
Schematic picture of four different NTs binding to ACP-TrkA. The ACP-TrkA construct and the four ligands investigated for receptor binding [104] are schematically depicted. NGF, NGF R100E mutant (mutNGF, related to HSANV disease [132]), proNGF and NT-3 all bind to the extracellular domain of TrkA receptor but with different affinity, as quantified by the Kd (dissociation constant) values (see the color-coded arrowheads referring to the corresponding Kd values, which are taken from: ≠ [133]; * [134]; † [135]). The evoked physiological responses are also different among the four ligands and are summarized at the C-terminus of the receptor, highlighted by arrowheads with the same color-code. Intracellular effectors recruited at phosphorylated tyrosine residues and leading to the activation of the MAP kinase, the Akt and PLCγ signaling pathways, upon TrkA-NT binding are also schematically depicted. The numbering of tyrosine residues refers to the rat TrkA cDNA sequence. Note that while Y499 and 794 only have recruitment function, Y683/4 constitute with Y679 (not depicted) the activation loop of tyrosine kinase activity. The figure has been adapted from [104].