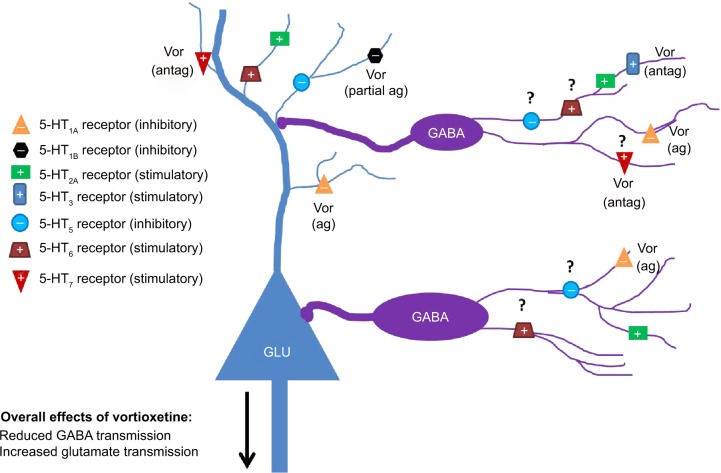
Figure 2.
Serotonergic influence on GABAergic neurotransmission in limbic system brain regions. Serotonergic heteroreceptors expressed on GABAergic interneurons and glutamatergic principal cells can modulate the excitatory state of neural networks associated with the control of cognitive function and mood. Vortioxetine may be an example of a drug that inhibits GABA neurotransmission via serotonergic mechanisms. Question marks denote receptors where expression on GABAergic interneurons has been indirectly suggested but no immunohistochemical verification exists for limbic brain regions.
Abbreviations: ag, agonist; antag, antagonist; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GLU, glutamate; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; Vor, vortioxetine.