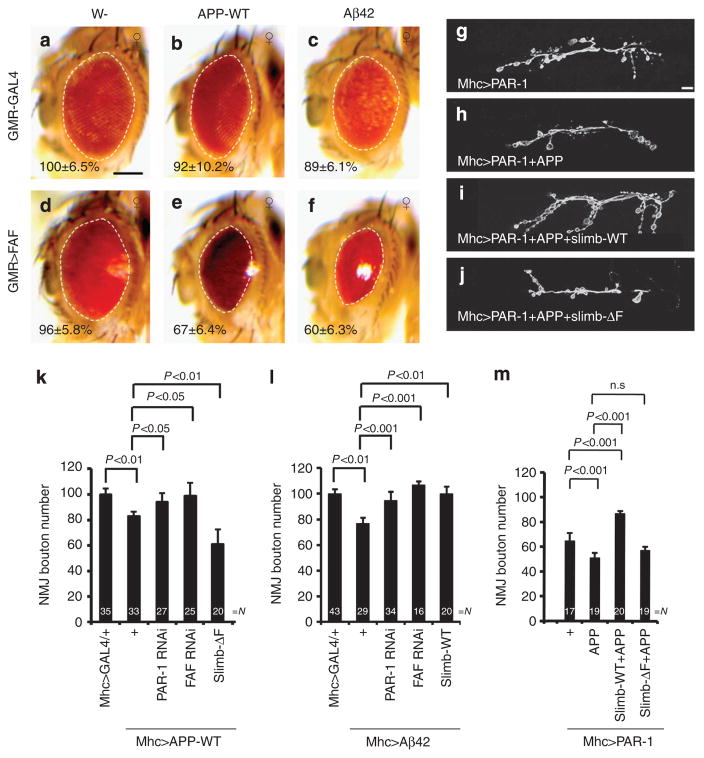
Figure 5. Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of PAR-1 mediates the toxicity of APP and Aβ–42.
(a–f) Genetic interaction between APP/Aβ-42 and FAF in the retina. Images of female flies are shown. All flies were grown at 25 °C. The genotypes are: GMR-Gal4/ +control (a), GMR-Gal4>UAS-APP-WT (b), GMR-Gal4>UAS-Aβ-42 (c), GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381 (d), GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381 +UAS-APP-WT (e) and GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381 +UAS-Aβ-42 (f) (n =16, 18, 16, 17, 16 and 16 animals, respectively). Statistically significant differences are P<0.01 (GMR-Gal4/ +control, GMR-Gal4>UAS-Aβ-42) or P<0.001 (GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381, GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381 +UAS-APP-WT; GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381, GMR-Gal4>FAFEP381 +UAS-Aβ-42) as determined by Student’s t-test. Experiments were performed in triplicate. Dashed lines outline the eye contour. Values represent areas of retinal surface normalized with GMR-Gal4/ +control. Scale bar (a–f), 100 μm. (g–j) Representative anti-horseradish peroxidase immunostaining showing larval NMJ morphology of the following genotypes: Mhc-Gal4>UAS-PAR-1 (g), Mhc-Gal4>UAS-PAR-1 +UAS-APP-WT (h), Mhc-Gal4>UAS-PAR-1 +UAS-APP-WT UAS-Slimb-WT (i) and Mhc-Gal4>UAS-PAR-1 +UAS-APP-WT +UAS-Slimb-ΔF (j). Scale bar, 10 μm. (k–m) Quantification of NMJ bouton numbers showing genetic interactions among APP, PAR-1, Slimb and FAF (k), among Aβ-42, PAR-1, Slimb and FAF (l), or between APP +PAR-1 and Slimb (m). Flies were grown at 29 °C (k) or 25 °C (l,m). N indicates the number of animals analysed. The error bars represent means±s.e.m. P-values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test for each comparison. Experiments were performed in triplicate. n.s, not significant.